San Juan (, , ; Spanish for "Saint
John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Secon ...
") is the
capital city
A capital city or capital is the municipality holding primary status in a country, state, province, Department (country subdivision), department, or other subnational entity, usually as its seat of the government. A capital is typically a city ...
and most populous
municipality
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality'' may also mean the go ...
in the
Commonwealth of
Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and Unincorporated ...
, an
unincorporated territory
Territories of the United States are sub-national administrative divisions overseen by the federal government of the United States. The various American territories differ from the U.S. states and tribal reservations as they are not sove ...
of the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
. As of the
2020 census, it is the
57th-largest city under the jurisdiction of the United States, with a population of 342,259. San Juan was founded by
Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
colonists in 1521, who called it Ciudad de Puerto Rico ("City of Puerto Rico", Spanish for ''rich port city'').
Puerto Rico's capital is the third oldest European-established capital city in the Americas, after
Santo Domingo
, total_type = Total
, population_density_km2 = auto
, timezone = AST (UTC −4)
, area_code_type = Area codes
, area_code = 809, 829, 849
, postal_code_type = Postal codes
, postal_code = 10100–10699 ( Distrito Nacional)
, webs ...
, in the
Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with ...
, founded in 1496, and
Panama City
Panama City ( es, Ciudad de Panamá, links=no; ), also known as Panama (or Panamá in Spanish), is the capital and largest city of Panama. It has an urban population of 880,691, with over 1.5 million in its metropolitan area. The city is locat ...
, in
Panama
Panama ( , ; es, link=no, Panamá ), officially the Republic of Panama ( es, República de Panamá), is a transcontinental country spanning the southern part of North America and the northern part of South America. It is bordered by Cos ...
, founded in 1521,
and is the
oldest European-established city under
United States sovereignty. Several historical buildings are located in San Juan; among the most notable are the city's former defensive forts,
Fort San Felipe del Morro
Castillo San Felipe del Morro, also known as El Morro, is a citadel built between 16th and 18th centuries in San Juan, Puerto Rico.[ww ...](_blank)
and
Fort San Cristóbal, and
La Fortaleza
La Fortaleza (lit., "The Fortress" ) is the official residence of the governor of Puerto Rico. It was built between 1533 and 1540 to defend the harbor of San Juan. The structure is also known as Palacio de Santa Catalina (Saint Catherine's Palac ...
, the oldest
executive mansion in continuous use in the Americas.
Today, San Juan is
Puerto Rico's most important seaport and is the island's financial, cultural, and
tourism center. The population of the
metropolitan statistical area
In the United States, a metropolitan statistical area (MSA) is a geographical region with a relatively high population density at its core and close economic ties throughout the area. Such regions are neither legally Incorporated town, incorporate ...
, including San Juan and the municipalities of
Bayamón,
Guaynabo
Guaynabo (, ) is a city, suburb of San Juan and municipality in the northern part of Puerto Rico, located in the northern coast of the island, north of Aguas Buenas, south of Cataño, east of Bayamón, and west of San Juan. Guaynabo is spr ...
,
Cataño,
Canóvanas,
Caguas
Caguas (, ) is a city and municipality of Puerto Rico located in the Central Mountain Range of Puerto Rico, south of San Juan and Trujillo Alto, west of Gurabo and San Lorenzo, and east of Aguas Buenas, Cidra, and Cayey. Caguas was founde ...
,
Toa Alta,
Toa Baja
Toa Baja (, ) is a town and municipality of Puerto Rico located in the northern coast, north of Toa Alta and Bayamón; east of Dorado; and west of Cataño. Toa Baja is spread over five barrios, including Toa Baja Pueblo (the downtown area and ...
,
Carolina and
Trujillo Alto
Trujillo Alto (, ) is a town and municipality of Puerto Rico located in the Northern Coastal Plain, on the boundary between the karst zone and Sierra de Luquillo, north of Caguas, and Gurabo; southeast of San Juan, and west of Carolina. Truji ...
, is about 2.443 million inhabitants; thus, about 76% of the population of Puerto Rico now lives and works in this area. San Juan is also a principal city of the
San Juan-Caguas-Fajardo Combined Statistical Area. The city has been the host of events within the sports community, including the 1979
Pan American Games
The Pan American Games (also known colloquially as the Pan Am Games) is a continental multi-sport event in the Americas featuring summer sports, in which thousands of athletes participate in a variety of competitions. The competition is held ...
; 1966
Central American and Caribbean Games
The Central American and Caribbean Games (CAC or CACGs) are a multi-sport regional championship event, held quadrennial (once every four years), typically in the middle (even) year between Summer Olympics. The games are for countries in Cent ...
; events of the 2006, 2009 and 2013
World Baseball Classic
The World Baseball Classic (WBC) is an international baseball tournament sanctioned from 2006 to 2013 by the International Baseball Federation (IBAF) and after 2013 by World Baseball Softball Confederation (WBSC) in partnership with Major Lea ...
s; the
Caribbean Series
The Caribbean Series (''Spanish'': ''Serie del Caribe''), also called Caribbean World Series, is the highest tournament for professional baseball teams in Latin America. The tournament location is rotated annually among the countries and is norma ...
and the
Special Olympics
Special Olympics is the world's largest sports organization for children and adults with intellectual disabilities and physical disabilities, providing year-round training and activities to 5 million participants and Unified Sports partners in ...
and
MLB
Major League Baseball (MLB) is a professional baseball organization and the oldest major professional sports league in the world. MLB is composed of 30 total teams, divided equally between the National League (NL) and the American League (AL), ...
San Juan Series in 2010.
History
Pre-Columbian era
The
Taíno
The Taíno were a historic indigenous people of the Caribbean whose culture has been continued today by Taíno descendant communities and Taíno revivalist communities. At the time of European contact in the late 15th century, they were the pri ...
people were the indigenous inhabitants of the area before the arrival of the
Europeans to the island of
Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and Unincorporated ...
in 1493. Remains of a small indigenous fishing village have been found in
Puerta de Tierra
Puerta de Tierra is a ''subbarrio'' (subdistrict) occupying the eastern portion of the Islet of San Juan and the ''barrio'' of San Juan Antiguo in the municipality of San Juan, Puerto Rico. The name Puerta de Tierra (Spanish for ''land gate'') ...
where the
Puerto Rico National Guard Museum stands today, however most archaeological sites in the region have been destroyed and lost throughout the colonial history. The area of San Juan used to be the boundary between the tribal regions (yucayeques) of ''Guaynabo'' and ''Haimanio'', led by the chiefs (
caciques
A ''cacique'' (Latin American ; ; feminine form: ''cacica'') was a tribal chieftain of the Taíno people, the indigenous inhabitants at European contact of the Bahamas, the Greater Antilles, and the northern Lesser Antilles. The term is a Spa ...
)
Mabo and
Yuisa (also known as Loaíza), respectively, at the time of the arrival of the
Spanish conquistadors
Conquistadors (, ) or conquistadores (, ; meaning 'conquerors') were the explorer-soldiers of the Spanish Empire, Spanish and Portuguese Empires of the 15th and 16th centuries. During the Age of Discovery, conquistadors sailed beyond Europe to ...
.
Founding
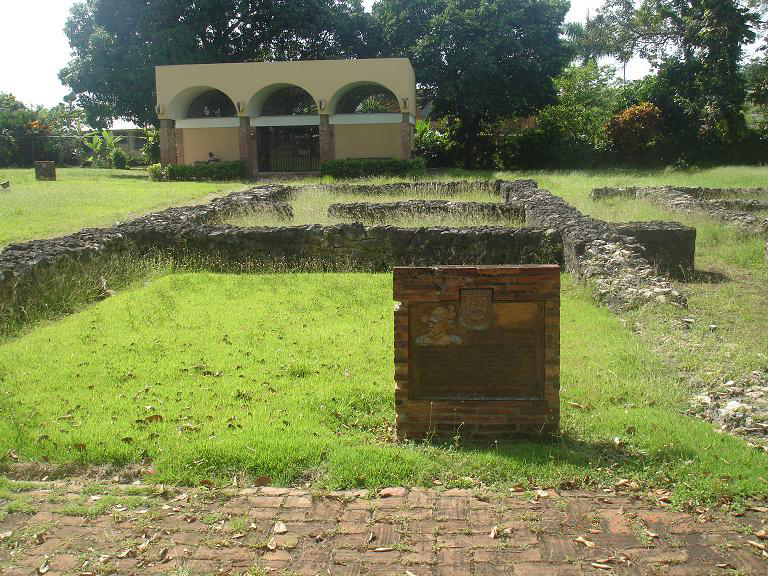

In 1508,
Juan Ponce de León founded the original settlement which he called
Caparra. It was named after the province of
Cáceres in Spain, the birthplace of
Nicolás de Ovando
Frey Nicolás de Ovando y Cáceres (1460 – 29 May 1511 or 1518) was a Spanish soldier from a noble family and a Knight of the Order of Alcántara, a military order of Spain. He was Governor of the Indies ( Hispaniola) from 1502 until 1509, se ...
, then the Governor of Spain's Caribbean territories. Today, it is part of the
Pueblo Viejo district of
Guaynabo
Guaynabo (, ) is a city, suburb of San Juan and municipality in the northern part of Puerto Rico, located in the northern coast of the island, north of Aguas Buenas, south of Cataño, east of Bayamón, and west of San Juan. Guaynabo is spr ...
, directly to the west of the modern municipality of San Juan. A year later, the settlement was moved to a site then called Puerto Rico, Spanish for "rich port" or "good port", after its similar geographical features to the town of
Puerto Rico de Gran Canaria
Puerto Rico de Gran Canaria is a holiday resort situated on the south-west coast of the Spanish island of Gran Canaria. Temperatures in the winter remain around 20-25 °C while there is an average of less than three days per month of pre ...
in the
Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; es, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to the African mainland, they are west of Morocc ...
.
The
local Catholic diocese, the second oldest in the Americas and the oldest in the United States, was founded in the newly built settlement on August 8 of 1511. In 1521, the newer settlement was given its formal name: ''Ciudad de Puerto Rico de San Juan Bautista''. Many of the oldest European-founded institutions in the Western Hemisphere, such as the Santo Tomás de Aquino Convent and the Nuestra Señora de la Concepción Hospital, were established during this time in San Juan.
The ambiguous use of ''San Juan Bautista'' and ''Puerto Rico'' for both the city and the island in time led to a reversal in practical use by most inhabitants: by 1746 the name for the city (Puerto Rico) had become that of the entire island, leading to the city being identified as ''Puerto Rico de Puerto Rico'' on maps of the era.
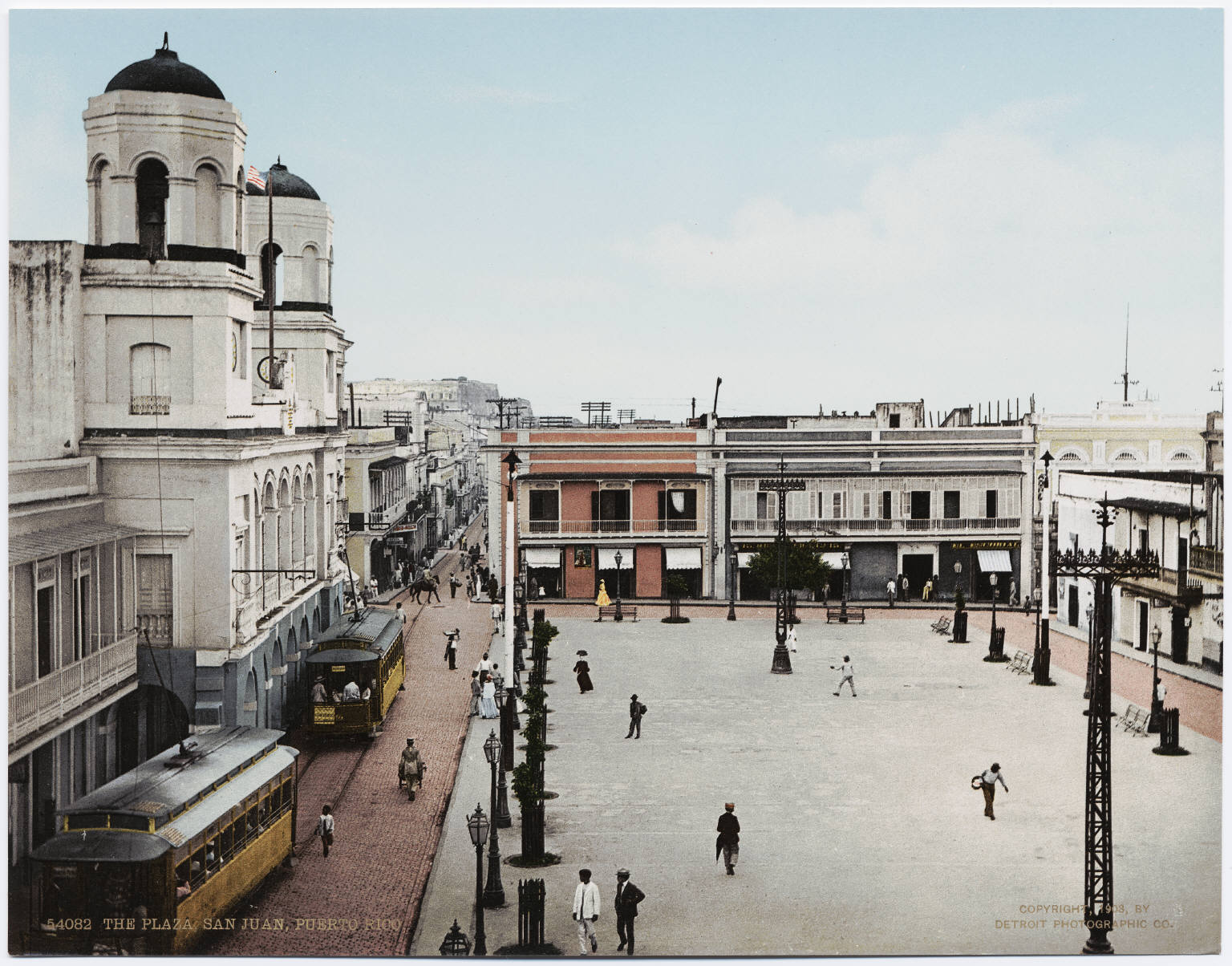
Spanish Colonial era
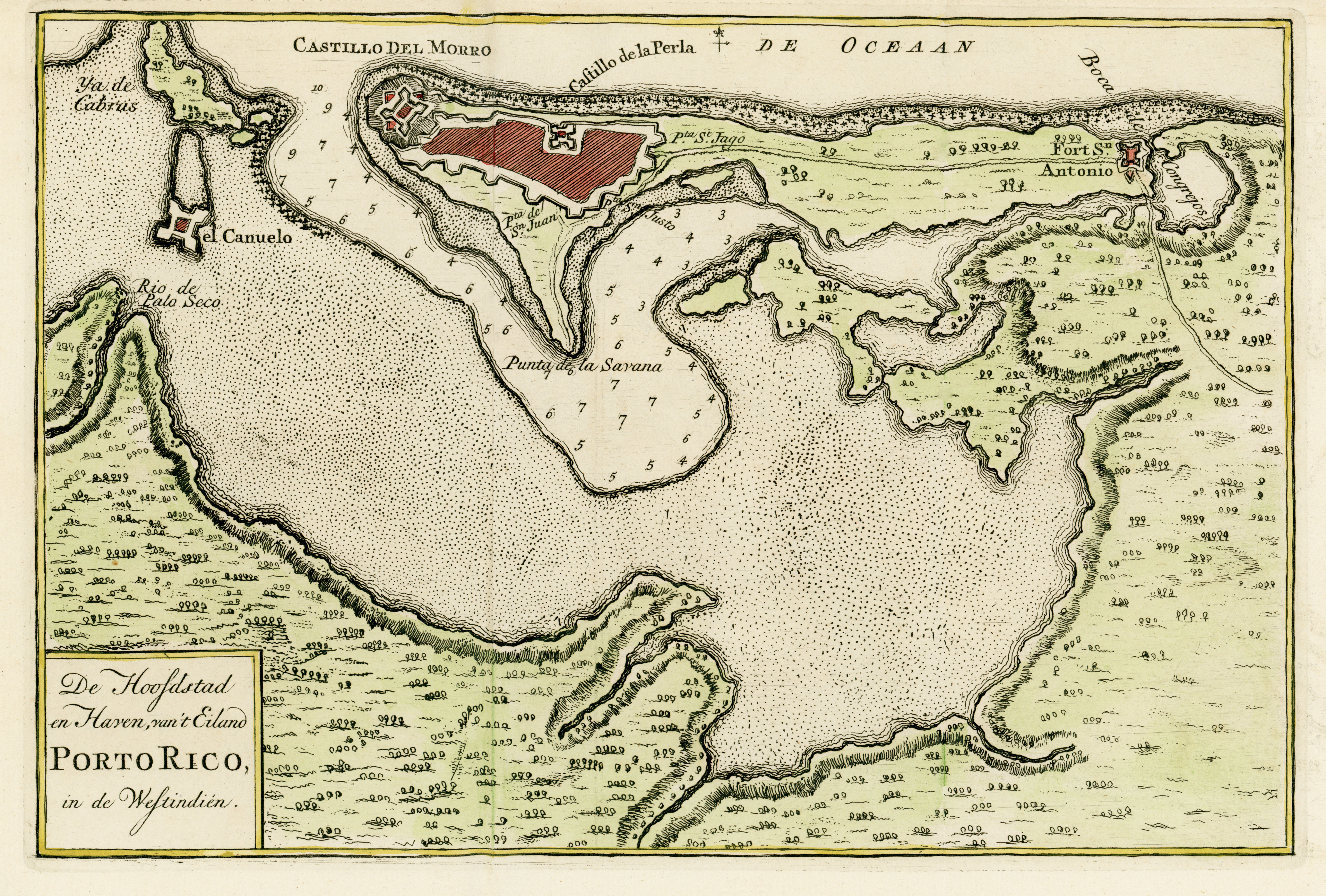
San Juan, as a settlement of the
Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
, was used by merchant and military ships traveling from Spain as the first stopover in the
Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
. Because of its prominence in the Caribbean, a network of fortifications was built to protect the transports of gold and silver from the
New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. ...
to Europe. Because of the rich cargoes, San Juan became a target of the foreign powers of the time.
San Juan underwent attacks from the English led by
Sir Francis Drake
Sir Francis Drake ( – 28 January 1596) was an English explorer, sea captain, privateer, slave trader, naval officer, and politician. Drake is best known for his circumnavigation of the world in a single expedition, from 1577 to 1580 ( ...
in 1595 (in what is known as the
Battle of Puerto Rico
The Battle of San Juan (1595) was a Spanish victory during the Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604), Anglo–Spanish War. This war broke out in 1585 and was fought not only in the European theatre but in Spain's American colonies. After emerging from ...
) and by
George Clifford,
Earl of Cumberland
The title of Earl of Cumberland was created in the Peerage of England in 1525 for the 11th Baron de Clifford.''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, Oxford University Press'', 2004. It became extinct in 1643. The dukedom of Cumberland was cr ...
, in 1598. Artillery from San Juan's fort,
El Morro, repelled Drake; however, Clifford managed to land troops and lay siege to the city.
After a few months of English occupation, Clifford was forced to abandon the siege when his troops began to suffer from exhaustion and sickness. In 1625 the city was sacked by Dutch forces led by Captain
Balduino Enrico (also known as Boudewijn Hendricksz/Bowdoin Henrick), but El Morro withstood the assault and was not taken. The Dutch were counterattacked by Captain
Juan de Amézqueta
Juan de Amézqueta (born c. 1595), was a captain in the Puerto Rican Militia who defended Puerto Rico from an invasion by the Dutch in 1625. He fought and wounded Captain Balduino Enrico (Boudewijn Hendricksz) who was ordered by the Dutch Governm ...
and 50 members of the civilian militia on land and by the cannons of the Spanish troops in El Morro castle. The land battle left 60 Dutch soldiers dead and Enrico with a sword wound to his neck which he received from the hands of Amézqueta.
The Dutch ships at sea were boarded by Puerto Ricans who defeated those aboard. After a long battle, the Spanish soldiers and volunteers of the city's militia were able to defend the city from the attack and save the island from an invasion. On October 21, Enrico set
La Fortaleza
La Fortaleza (lit., "The Fortress" ) is the official residence of the governor of Puerto Rico. It was built between 1533 and 1540 to defend the harbor of San Juan. The structure is also known as Palacio de Santa Catalina (Saint Catherine's Palac ...
and the city ablaze. Captains Amézqueta and Andrés Botello decided to put a stop to the destruction and led 200 men in an attack against the enemy's front and rear guard. They drove Enrico and his men from their trenches and into the ocean in their haste to reach their ships.
[The History of Puerto Rico From the Spanish Discovery to the American Occupation / Middeldyk, R.A. Van Identifier: etext12272 The History of Puerto Rico From the Spanish Discovery to the American Occupation](_blank)
The British
attack in 1797, during the
French Revolutionary Wars
The French Revolutionary Wars (french: Guerres de la Révolution française) were a series of sweeping military conflicts lasting from 1792 until 1802 and resulting from the French Revolution. They pitted French First Republic, France against Ki ...
, led by
Sir Ralph Abercromby
Lieutenant General Sir Ralph Abercromby (7 October 173428 March 1801) was a British soldier and politician. He rose to the rank of lieutenant-general in the British Army, was appointed Governor of Trinidad, served as Commander-in-Chief, Ir ...
(who had just conquered
Trinidad
Trinidad is the larger and more populous of the two major islands of Trinidad and Tobago. The island lies off the northeastern coast of Venezuela and sits on the continental shelf of South America. It is often referred to as the southernmos ...
). His army laid siege to the city but was forced to withdraw in defeat as the Puerto Rican defenses proved more resilient than those of Trinidad. Various events and circumstances, including liberalized commerce with Spain, the opening of the island to immigrants as a direct result of the
Royal Decree of Graces of 1815
The Royal Decree of Graces of 1815 ( Spanish: ''Real Cédula de Gracias'') is a legal order approved by the Spanish Crown in the early half of the 19th century to encourage Spaniards and, later, Europeans of non-Spanish origin, to settle in and po ...
, and the colonial revolutions, led to an expansion of San Juan and other Puerto Rican settlements in the late 18th and early 19th century.
Spanish-American War

On May 8, 1898, United States Navy ships, among them , , , , and , commanded by
Rear Admiral William T. Sampson
William Thomas Sampson (February 9, 1840 – May 6, 1902) was a United States Navy rear admiral known for his victory in the Battle of Santiago de Cuba during the Spanish–American War.
Biography
He was born in Palmyra, New York, and entered ...
arrived at San Juan Bay. captured the Spanish freighter ''Rita'' in San Juan Bay, thus being the first hostile encounter between the warring sides in Puerto Rico. On May 9, ''Yale'' fought a brief battle with an
auxiliary cruiser
An armed merchantman is a merchant ship equipped with guns, usually for defensive purposes, either by design or after the fact. In the days of sail, piracy and privateers, many merchantmen would be routinely armed, especially those engaging in ...
of Spain, name unknown, resulting in a Spanish victory. Around this time, Captain
Ángel Rivero Méndez
Ángel Rivero Méndez (1862 – February 23, 1930) was a Puerto Rican soldier, writer, journalist and a businessman. Rivero Méndez was a Captain in the Spanish Army during the Spanish–American War and is credited with ordering the first shot ...
was assigned the command of the Spanish forces in the fortress of
San Cristóbal in San Juan. On May 10, ''Yale'' returned to San Juan Bay, Rivero-Méndez ordered his men to open fire upon ''Yale'' using an Ordoñez 15-centimeter cannon, thus becoming the first attack against the Americans in Puerto Rico during the
Spanish–American War
, partof = the Philippine Revolution, the decolonization of the Americas, and the Cuban War of Independence
, image = Collage infobox for Spanish-American War.jpg
, image_size = 300px
, caption = (clock ...
.
For his actions, Captain Rivero-Méndez was awarded the "Cruz de la Orden de Mérito Militar" (The Cross of the Order of the Military Merit) first class.
The residents of San Juan were furious with Rivero and blamed him for the destruction caused to their city by the American bombardments. Nothing came of those accusations and Capt. Rivero-Méndez was ordered to turn over the keys of all the military installations in San Juan to Captain Henry A. Reed of the U.S. Army after the
Treaty of Paris of 1898
The Treaty of Peace between the United States of America and the Kingdom of Spain, commonly known as the Treaty of Paris of 1898 ( fil, Kasunduan sa Paris ng 1898; es, Tratado de París de 1898), was a treaty signed by Spain and the United Stat ...
was signed.
On July 25, General
Nelson A. Miles
Nelson Appleton Miles (August 8, 1839 – May 15, 1925) was an American military general who served in the American Civil War, the American Indian Wars, and the Spanish–American War.
From 1895 to 1903, Miles served as the last Commanding Gen ...
landed at
Guánica (in southwestern Puerto Rico) with 3,300 soldiers in what was known as the
Puerto Rican Campaign. The American troops found some resistance and engaged the Spanish and Puerto Rican troops in battle, the most notable of these the battles of
Yauco
Yauco () is a town and municipality in southern Puerto Rico. Although the downtown is inland, the municipality stretches to a southern coast facing the Caribbean Sea. Yauco is located south of Maricao, Lares and Adjuntas; east of Sabana G ...
and
Asomante. All military actions in Puerto Rico were suspended August 13, 1898, after President
William McKinley
William McKinley (January 29, 1843September 14, 1901) was the 25th president of the United States, serving from 1897 until his assassination in 1901. As a politician he led a realignment that made his Republican Party largely dominant in ...
and French Ambassador
Jules Cambon
Jules-Martin Cambon (5 April 1845 – 19 September 1935) was a French diplomat and brother to Paul Cambon. As the ambassador to Germany (1907–1914) he worked hard to secure a friendly détente. He was frustrated by French leaders such as Raym ...
, acting on behalf of the Spanish government, signed an
armistice
An armistice is a formal agreement of warring parties to stop fighting. It is not necessarily the end of a war, as it may constitute only a cessation of hostilities while an attempt is made to negotiate a lasting peace. It is derived from the ...
.
Spain ceded the island to the United States later the same year by signing the
Treaty of Paris Treaty of Paris may refer to one of many treaties signed in Paris, France:
Treaties
1200s and 1300s
* Treaty of Paris (1229), which ended the Albigensian Crusade
* Treaty of Paris (1259), between Henry III of England and Louis IX of France
* Trea ...
.
20th-century

Camp Las Casas
Camp Las Casas was a United States military installation established in Santurce, Puerto Rico in 1904. The camp was the main training base of the "Porto Rico Regiment of Infantry," On January 15, 1899, the military government changed the name of ...
, located in the district of
Santurce, served as the main training camp for the Puerto Rican soldiers prior to World War I and World War II; the majority of the men trained in this facility were assigned to the "Porto Rico Regiment of Infantry" which was renamed the
65th Infantry Regiment
The 65th Infantry Regiment, nicknamed "The Borinqueneers" during the Korean War for the original Taíno Indian name for Puerto Rico (Borinquen), is a Puerto Rican regiment of the United States Army. The regiment's motto is ''Honor et Fidelita ...
of the United States Army by the Reorganization Act of June 4, 1920. The 65th Infantry was deactivated in 1956 and became the only unit ever to be transferred from an active Army component to the
Puerto Rico National Guard
The Puerto Rico National Guard (PRNG) – es, Guardia Nacional de Puerto Rico– is the national guard of the U.S. Commonwealth of Puerto Rico. The Constitution of the United States specifically charges the National Guard with dual federal and s ...
.
Lieutenant
Teófilo Marxuach
Lieutenant Colonel Teófilo Marxuach, (July 28, 1877 – November 8, 1939), was the person who ordered the first shots fired in World War I on behalf of the United States on an armed German supply ship trying to force its way out of the San Juan ...
(retired as a Lieutenant Colonel), a native of
Arroyo, Puerto Rico
Arroyo () is a town and municipality located along the southern coast of Puerto Rico and bordered by the Caribbean Sea, east of the municipality of Guayama and northwest of the municipality of Patillas. Arroyo is spread over 5 barrios and Ar ...
, fired the first shot in what is considered to be the first shot of World War I fired by the regular armed forces of the United States against any ship flying the colors of the
Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,german: Mittelmächte; hu, Központi hatalmak; tr, İttifak Devletleri / ; bg, Централни сили, translit=Tsentralni sili was one of the two main coalitions that fought in ...
.
["US Naval Institute Proceedings"; "A Breach of Neutrality"; by: Lt. Isaiah Olch, US Navy; Vol. 62; July - December 1936] Marxuach, who was a member of the "Porto Rico Regiment of Infantry" and Officer of the Day, on March 25, 1915, opened fire on the ''Odenwald'', an armed German supply vessel, when it was trying to force its way out of San Juan's bay.
The shots ordered by Lt. Marxuach were the first fired by the United States in World War I.
In 1919,
Félix Rigau Carrera
Félix Rigau Carrera (August 30, 1894 – October 13, 1954), known as (The Eagle from Sabana Grande), was the first Puerto Rican pilot and the first Puerto Rican pilot to fly on air mail carrying duties in Puerto Rico.
Early years
Rigau Carrer ...
, "El Aguila de Sabana Grande" (The Eagle from
Sabana Grande), the first Puerto Rican pilot, became the first native Puerto Rican to fly an aircraft in the island when he flew his
Curtiss JN-4
The Curtiss JN "Jenny" was a series of biplanes built by the Curtiss Aeroplane Company of Hammondsport, New York, later the Curtiss Aeroplane and Motor Company. Although the Curtiss JN series was originally produced as a training aircraft for th ...
from Las Casas. At the time, the area was used by the military as an air base and it was also Puerto Rico's first commercial airport, and Rigau Carrera was allowed to perform his historic flight from the airfield.
["El Mundo"; "Fallece El Aguila - Fue Primer Boricua Manejo Avion en la Isla" (Spanish); by: Malen Rojas Daporte; October 20, 1954; Number 13,448] Camp Las Casas was eventually closed down, and in 1950 a public housing project by the name of
Residencial Fray Bartolome de Las Casas was constructed on its former location.
On January 2, 1947, the people of San Juan elected
Felisa Rincón de Gautier
Felisa Rincón de Gautier (born Felisa Rincón Marrero)This name uses Spanish marriage naming customs; the first is the maiden family name '' "Rincón"'' and the second or matrimonial family name is ''"Gautier"''. (also known as Doña Fela) (Janua ...
(also known as Doña Fela) (1897–1994) as their mayor. Thus, she became the first woman to be elected as the mayor of a capital city in any of the Americas. During the
Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
era, she ordered the establishment of the island's first Civil Defense system under the directorship of Colonel
Gilberto José Marxuach
Colonel Gilberto José Marxuach a.k.a. "The Father of the San Juan Civil Defense" (November 19, 1910 – April 18, 1957), was a former officer in the United States Army who in 1951 founded and became the first director of the Civil Defense in ...
(Teófilo's son). Rincón de Gautier served as mayor until January 2, 1969.
On October 30, 1950, San Juan was the scene of the
San Juan Uprising, one of many uprisings which occurred in various towns and cities in Puerto Rico, by the
Puerto Rican Nationalist Party
The Nationalist Party of Puerto Rico ( es, Partido Nacionalista de Puerto Rico, PNPR) is a Puerto Rican political party founded on September 17, 1922, in San Juan, Puerto Rico. Its primary goal is to work for Puerto Rico's independence. The P ...
against the governments of Puerto Rico and the United States. Among the uprising's main objective was to attack La Fortaleza and the
United States Federal Court House Building in
Old San Juan
Old San Juan ( es, Viejo San Juan) is a historic district located at the "northwest triangle" of the islet of San Juan. Its area roughly correlates to the Ballajá, Catedral, Marina, Mercado, San Cristóbal, and San Francisco sub-barrios (s ...
. The "La Fortaleza battle", which ensued between the nationalists and the police lasted 15 minutes and ended when four of the five attackers were killed.
[''El ataque Nacionalista a La Fortaleza''; by Pedro Aponte Vázquez; Page 2; Publisher: Publicaciones RENÉ; ]
21st-century
San Juan has experienced periods of both stagnation and development in the recent years.
Gentrification
Gentrification is the process of changing the character of a neighborhood through the influx of more Wealth, affluent residents and businesses. It is a common and controversial topic in urban politics and urban planning, planning. Gentrification ...
has been noticeable in areas of the city such as
Loíza Street in
Santurce and
Santa Rita in Río Piedras. In recent years the city has been the location of multiple strikes and protests, such as the
2001 protests against the
United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
in the island municipality of
Vieques
Vieques (; ), officially Isla de Vieques, is an island and municipality of Puerto Rico, in the northeastern Caribbean, part of an island grouping sometimes known as the Spanish Virgin Islands. Vieques is part of the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, ...
, the
2010 and 2011 University of Puerto Rico strikes, and the
2019 protests against Governor
Ricardo Rosselló which resulted in his resignation.
On September 20, 2017,
Hurricane Maria
Hurricane Maria was a deadly Saffir–Simpson scale#Category 5, Category 5 Tropical cyclone, hurricane that devastated the northeastern Caribbean in September 2017, particularly Dominica, Saint Croix, and Puerto Rico. It is regarded as the wo ...
made a direct impact in Puerto Rico, causing widespread damage and a collapse of the infrastructure in San Juan and the rest of Puerto Rico. The damage caused in 2017 was extensive, affecting the electricity, potable water supplies, transportation, and communication, but significant progress had been made in the capital by April 2019, and particularly by October 2019. This was significant for tourism, which had rebounded by October of that year and was close to the pre-Maria era.
San Juan today remains an important cultural, financial and industrial center not only of Puerto Rico but of the Caribbean region. As the biggest industrial center of Puerto Rico, it is the home of industries such as tobacco processors, breweries, refining facilities for petroleum and sugar, and distillers of rum as well as manufacturers of metal products, cement, pharmaceuticals, and clothing. The
Puerto Rico Convention Center
The Dr. Pedro Rosselló González Puerto Rico Convention Center (PRCC) (or ''Centro de Convenciones de Puerto Rico Dr. Pedro Rosselló González'' in Spanish), or simply Puerto Rico Convention Center, is a convention center located in Isla Gr ...
, opened in 2005, is the largest of its kind in the Caribbean and one of the most advanced in the Americas.
File:La recuperación de la isla de Puerto Rico por el gobernador de la isla, Juan de Haro. Por Eugenio Cajés..jpg, A 17th-century Spanish painting commemorating Captain Juan de Amézqueta
Juan de Amézqueta (born c. 1595), was a captain in the Puerto Rican Militia who defended Puerto Rico from an invasion by the Dutch in 1625. He fought and wounded Captain Balduino Enrico (Boudewijn Hendricksz) who was ordered by the Dutch Governm ...
's victory and Enrico
Enrico is both an Italian masculine given name and a surname, Enrico means homeowner, or king, derived from ''Heinrich'' of Germanic origin. It is also a given name in Ladino. Equivalents in other languages are Henry ( English), Henri ( French), ...
's defeat at Puerto Rico de San Juan; by Eugenio Caxés
Eugenio Caxés (1574/75 – 15 December 1634) was a Spanish painter of the Baroque period.
Biography
He was born into a Florentine family in Madrid, and wrote his name in a variety of ways (Cajés, Cazés, Caxesi, and Caxete). His fathe ...
, Museo del Prado.
File:El Morro Castle, San Juan, Puerto Rico.jpg, Castle San Felipe del Morro, built in the 16th century.
File:Félix Rigau Carrera.jpg, Rigau Carrera poses in his plane, 1919.
File:Teofilo Marxuach.jpg, Lieutenant Teofilo Marxuach
File:Calle de Rafael Cordero in San Juan, Puerto Rico LOC 2179157820.jpg, Rafael Cordero Street in Old San Juan
Old San Juan ( es, Viejo San Juan) is a historic district located at the "northwest triangle" of the islet of San Juan. Its area roughly correlates to the Ballajá, Catedral, Marina, Mercado, San Cristóbal, and San Francisco sub-barrios (s ...
by Jack Delano
Jack Delano (born Jacob Ovcharov; August 1, 1914 – August 12, 1997) was a Ukrainian immigrant who became an accomplished photographer for the Works Progress Administration, United Fund, and most notably, the Farm Security Administration (FSA). ...
, 1941.
File:La Fortaleza attack-1950.jpg, The bodies of two nationalists lie on the ground after their attack on La Fortaleza
La Fortaleza (lit., "The Fortress" ) is the official residence of the governor of Puerto Rico. It was built between 1533 and 1540 to defend the harbor of San Juan. The structure is also known as Palacio de Santa Catalina (Saint Catherine's Palac ...
(1950)
Geography

San Juan is located along the north-eastern coast of Puerto Rico in the Northern Plains region. It lies south of the Atlantic Ocean; north of
Caguas
Caguas (, ) is a city and municipality of Puerto Rico located in the Central Mountain Range of Puerto Rico, south of San Juan and Trujillo Alto, west of Gurabo and San Lorenzo, and east of Aguas Buenas, Cidra, and Cayey. Caguas was founde ...
and
Trujillo Alto
Trujillo Alto (, ) is a town and municipality of Puerto Rico located in the Northern Coastal Plain, on the boundary between the karst zone and Sierra de Luquillo, north of Caguas, and Gurabo; southeast of San Juan, and west of Carolina. Truji ...
; east of
Guaynabo
Guaynabo (, ) is a city, suburb of San Juan and municipality in the northern part of Puerto Rico, located in the northern coast of the island, north of Aguas Buenas, south of Cataño, east of Bayamón, and west of San Juan. Guaynabo is spr ...
; and west of
Carolina. The city occupies an area of , of which, (37.83%) is water. San Juan's main water bodies are
San Juan Bay
San Juan Bay ( es, Bahía de San Juan) is the bay and main inlet adjacent to Old San Juan in northeastern Puerto Rico. It is about in length, the largest body of water in an estuary of about of channels, inlets and eight interconnected lagoons ...
and two natural lagoons, the
Condado and
San José. At almost 1,030 feet (314 m) above sea level, the highest point in the municipality of San Juan is located on an unnamed hill on the ''Morcelo'' sector of
Caimito, close to the municipal border with
Caguas
Caguas (, ) is a city and municipality of Puerto Rico located in the Central Mountain Range of Puerto Rico, south of San Juan and Trujillo Alto, west of Gurabo and San Lorenzo, and east of Aguas Buenas, Cidra, and Cayey. Caguas was founde ...
.
The municipality of San Juan is surrounded by the
San Juan metropolitan area, particularly the highly urbanized municipalities of
Guaynabo
Guaynabo (, ) is a city, suburb of San Juan and municipality in the northern part of Puerto Rico, located in the northern coast of the island, north of Aguas Buenas, south of Cataño, east of Bayamón, and west of San Juan. Guaynabo is spr ...
,
Trujillo Alto
Trujillo Alto (, ) is a town and municipality of Puerto Rico located in the Northern Coastal Plain, on the boundary between the karst zone and Sierra de Luquillo, north of Caguas, and Gurabo; southeast of San Juan, and west of Carolina. Truji ...
and
Carolina. These municipalities, together with
Bayamón and
Cataño, form what is locally referred to as the ''Área Metro'', the core of the wider San Juan metropolitan area. In total 41 municipalities are included in the entire metropolitan area extends throughout the island's northern coast and central eastern regions.
[www.whitehouse.gov](_blank)
Office of Management and Budget I The White House - Puerto Rico Metropolitan Statistical Area - Code 41980 - ''Revised Delineations of Metropolitan Statistical Areas as of 2013 Census Bureau''. Retrieved 2015-11-09.
Climate
San Juan has a
tropical monsoon climate
An area of tropical monsoon climate (occasionally known as a sub-equatorial, tropical wet climate or a tropical monsoon and trade-wind littoral climate) is a tropical climate sub-type that corresponds to the Köppen climate classification category ...
(
Am). It has an average temperature of . Temperatures of or higher are seen on an average 79 days annually, more commonly occurring during the wetter months of the northern summer, especially if the winds come from the south.
In the winter, temperatures can drop to around . The average winter low is . The coolest temperature officially recorded was on March 3, 1957, and the hottest was on October 9, 1981.
The record cold daily maximum is on February 4, 1935. The record warm daily minimum is on August 11, 1995, the most recent of four occasions.
With a mean minimum of 67 °F (19 C), San Juan is in USDA plant
hardiness zone 13B the highest category. Rainfall is well-distributed throughout the year. The months of January, February, and March are the driest. As March averages just of rain, the city falls under the
tropical monsoon category.
Rainfall averages , falling on an average 198.5 days per year.
Despite this dampness, the city averages 2,970 hours of sunshine per year, or just over of the possible total.
Annual rainfall has historically ranged from in 1991 to in 2010.

As with other parts of Puerto Rico and the Caribbean, San Juan is often blanketed by waves of
Saharan dust
Saharan dust is an aeolian mineral dust from the Sahara desert, the largest hot desert in the world. The desert spans just over 9 million square kilometers, from the Atlantic Ocean to the Red Sea, from the Mediterranean sea to the Niger River v ...
coming from the
Sahara across the Atlantic Ocean in
Northern Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in t ...
. Although beneficial to the tropical environment, these dust storms have recently become hazardous to human health causing haze and overheating in urban areas of the island. Due to San Juan's relatively flat geography, the dust often settles in these flat coastal regions of Puerto Rico as its flow is blocked by the higher altitude
Cordillera Central to the south, causing intense episodes of haze to settle for long periods of time, especially during periods of more scarce rainfall. Recent advancements include early warning systems to prepare the population for these intense episodes by both local authorities and the
EPA
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an independent executive agency of the United States federal government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon proposed the establishment of EPA on July 9, 1970; it be ...
.
Hurricane Maria
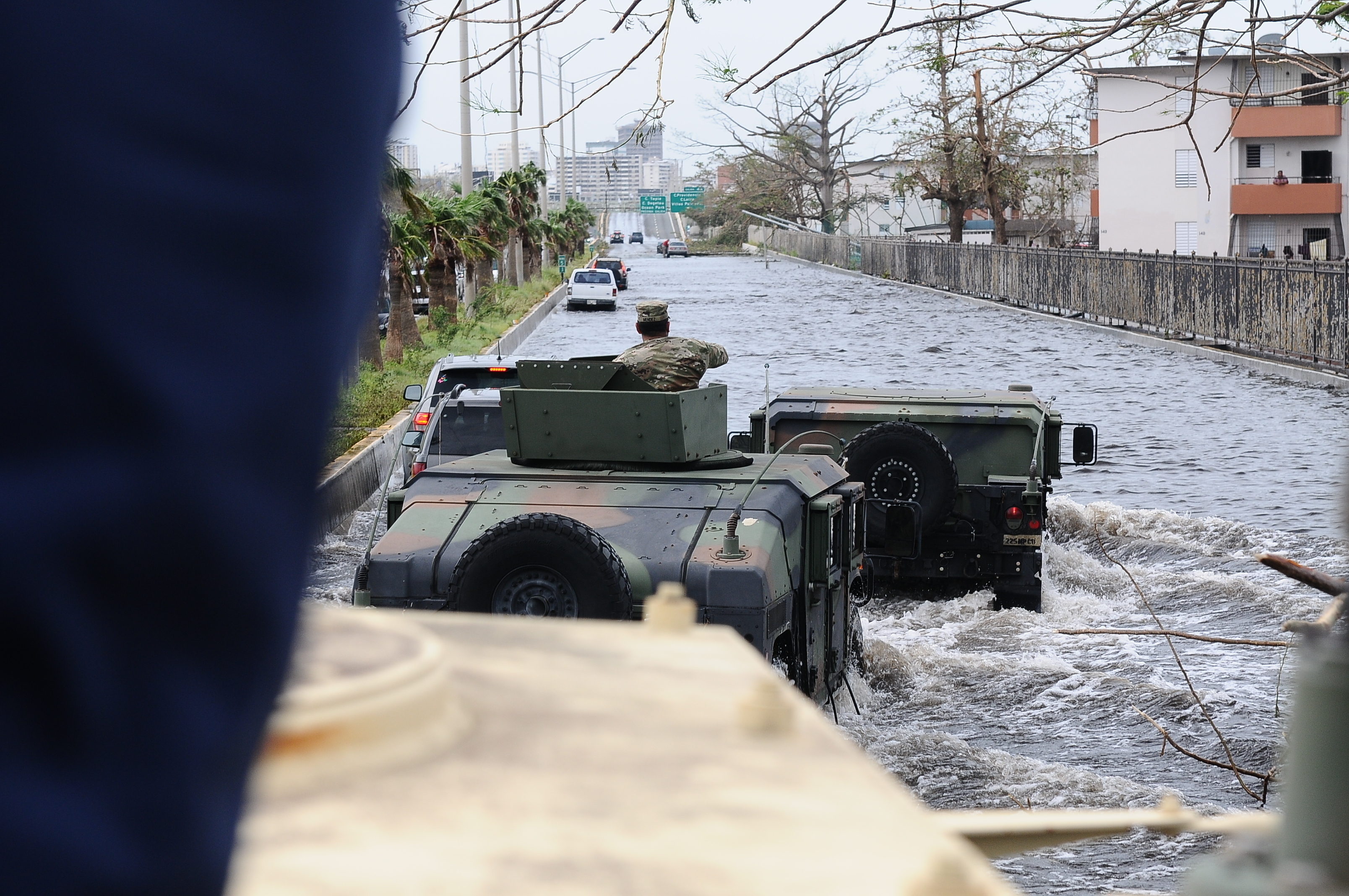

Hurricane Maria
Hurricane Maria was a deadly Saffir–Simpson scale#Category 5, Category 5 Tropical cyclone, hurricane that devastated the northeastern Caribbean in September 2017, particularly Dominica, Saint Croix, and Puerto Rico. It is regarded as the wo ...
made landfall in southeastern Puerto Rico on September 20, 2017.
Gusts up of to 113 mph (182 km/h) were reported in the capital city shortly before landfall in the municipality of
Yabucoa
Yabucoa () is a town and municipality in Puerto Rico located in the eastern region, north of Maunabo; south of San Lorenzo, Las Piedras and Humacao; and east of Patillas. Yabucoa is spread over 9 barrios and Yabucoa Pueblo (the downtown area ...
. The municipality of San Juan experienced widespread flooding in most coastal areas, and roofs were blown off from numerous structures. The neighborhood of
La Perla was largely destroyed. In the wider metropolitan area, flooding from
Lake La Plata produced flash floods that trapped residents of
Toa Baja
Toa Baja (, ) is a town and municipality of Puerto Rico located in the northern coast, north of Toa Alta and Bayamón; east of Dorado; and west of Cataño. Toa Baja is spread over five barrios, including Toa Baja Pueblo (the downtown area and ...
, and in
Cataño the Juana Matos neighborhood was estimated to be 80% destroyed.
At least eight people died from the flooding, while many were unaccounted for.
Beaches

San Juan is home to numerous
beaches
A beach is a landform alongside a body of water which consists of loose particles. The particles composing a beach are typically made from rock, such as sand, gravel, shingle, pebbles, etc., or biological sources, such as mollusc shel ...
, all of which are open to the public. All beaches of San Juan face the Atlantic Ocean. The
Islet of San Juan hosts Los Cables Beach and La Perla Beach next to the
Old San Juan
Old San Juan ( es, Viejo San Juan) is a historic district located at the "northwest triangle" of the islet of San Juan. Its area roughly correlates to the Ballajá, Catedral, Marina, Mercado, San Cristóbal, and San Francisco sub-barrios (s ...
district of
La Perla, the Capitolio Beach located immediately north of the Puerto Rico Capitol, Puerta de Tierra Beach along the ''Paseo de Puerta de Tierra'', and
El Escambrón Beach
El Escambrón Beach (Spanish: ''Balneario del Escambrón'') is a public-access beach located in the San Juan Antiguo sub-district (''subbarrio'') of Puerta de Tierra, next to the Luis Muñoz Rivera Park in San Juan, Puerto Rico. The beach and rec ...
at the northeastern edge of the islet. The latter is the most popular beach in the islet due to its shore being protected from the strong Atlantic Ocean waves by reefs that serve as natural
breakwaters
A breakwater is a permanent structure constructed at a coastal area to protect against tides, currents, waves, and storm surges. Part of a coastal management system, breakwaters are installed to minimize erosion, and to protect anchorages, h ...
. From east to west, the beaches in Santurce include
Ocean Park Beach (also known as Último Trolley Beach),
Condado Beach and
Playita del Condado
Playita del Condado is a beach located at the end of Ashford Avenue in Condado, Puerto Rico.
Playita del Condado
Playita del Condado is a beach near Condado Lagoon. It is near Miramar (Santurce), Miramar and Isla Grande (Santurce), Isla Gran ...
. Ocean Park Beach and El Condado Beach are the largest in the city and they host a large number of hotels and businesses that cater to tourists and beachgoers.
Beach erosion
As with other beaches across Puerto Rico and the Caribbean, the beaches of San Juan are currently under the threat of
coastal erosion
Coastal erosion is the loss or displacement of land, or the long-term removal of sediment and rocks along the coastline due to the action of waves, currents, tides, wind-driven water, waterborne ice, or other impacts of storms. The landwa ...
, particularly that of Ocean Park. The threat has become more evident recently and there are currently no state reports dedicated to the documentation or mitigation planning, according to oceanographer and geologist Maritza Barreto.
Parks
The municipality of San Juan contains numerous parks, including public parks, historic and heritage parks, nature reserves, protected natural areas, and recreational parks. These parks are managed by a number of entities such as the Municipality, the
Puerto Rico Department of Natural and Environmental Resources
The Puerto Rico Department of Natural and Environmental Resources (PRDNER) is the executive department of the government of Puerto Rico tasked with protecting, conserving, developing, and managing the natural and environmental resources in Pue ...
, the
National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an agency of the United States federal government within the U.S. Department of the Interior that manages all national parks, most national monuments, and other natural, historical, and recreational propertie ...
, the
University of Puerto Rico
The University of Puerto Rico ( es, Universidad de Puerto Rico, UPR) is the main public university system in the U.S. Commonwealth of Puerto Rico. It is a government-owned corporation with 11 campuses and approximately 58,000 students and 5,3 ...
and
conservation easement
In the United States, a conservation easement (also called conservation covenant, conservation restriction or conservation servitude) is a power invested in a qualified private land conservation organization (often called a "land trust") or gover ...
s.
San Juan Ecological Corridor

The San Juan Ecological Corridor is a conservation project by the
Government of Puerto Rico
The government of Puerto Rico is a republican form of government with separation of powers, subject to the jurisdiction and sovereignty of the United States.[riparian
A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a river or stream. Riparian is also the proper nomenclature for one of the terrestrial biomes of the Earth. Plant habitats and communities along the river margins and banks a ...]
ecosystems along the
Río Piedras
Rio or Río is the Portuguese, Spanish, Italian, and Maltese word for "river". When spoken on its own, the word often means Rio de Janeiro, a major city in Brazil.
Rio or Río may also refer to:
Geography Brazil
* Rio de Janeiro
* Rio do Sul, a ...
; the
Doña Inés Mendoza Urban Forest, a small urban forest located next to the Luis Muñoz Marín Foundation in
Sabana Llana Sur;
Los Capuchinos Forest, a forest which covers a small
karst area also in Sabana Llana Sur; the
New Millennium State Forest, one of the 20
state forests of Puerto Rico; the
San Juan Waterworks, consisting of the Old Piedras River Aqueduct and adjacent
historic district; and the University of Puerto Rico Botanical Garden, also known as the
San Juan Botanical Garden
The San Juan Botanical Garden, officially known as the Botanical Garden of the University of Puerto Rico, is located in the Caribbean city of San Juan, capital of Puerto Rico. This lush “urban garden” of native and exotic flora serves a ...
.
Historic parks
The
San Juan National Historic Site is home to
El Morro Esplanade, a large open area located between
El Morro and
Ballajá in
Old San Juan
Old San Juan ( es, Viejo San Juan) is a historic district located at the "northwest triangle" of the islet of San Juan. Its area roughly correlates to the Ballajá, Catedral, Marina, Mercado, San Cristóbal, and San Francisco sub-barrios (s ...
. The esplanade is located in the
promontory
A promontory is a raised mass of land that projects into a lowland or a body of water (in which case it is a peninsula). Most promontories either are formed from a hard ridge of rock that has resisted the erosive forces that have removed the so ...
which gives ''El Morro'' its name and it offers views of the
San Juan Bay
San Juan Bay ( es, Bahía de San Juan) is the bay and main inlet adjacent to Old San Juan in northeastern Puerto Rico. It is about in length, the largest body of water in an estuary of about of channels, inlets and eight interconnected lagoons ...
and the rest of San Juan. It is very popular for activities such as picnics,
stargazing and
kite flying
A kite is a tethered heavier-than-air or lighter-than-air craft with wing surfaces that react against the air to create lift and drag forces. A kite consists of wings, tethers and anchors. Kites often have a bridle and tail to guide the face ...
.
The district of the
Capitol of Puerto Rico
The Capitol of Puerto Rico ( es, Capitolio de Puerto Rico) is located on the Islet of San Juan just outside the walls of Old San Juan. The building is home to the bicameral Legislative Assembly, composed of the House of Representatives and ...
is home to the Iglesias Pantín and Rafael Hernández Marín parks, and a line of monuments located along Constitución Avenue which includes the ''Walkway of the Presidents'', the
Puerto Rico Police
The Puerto Rico Police Department ( es, Policía de Puerto Rico), officially the Puerto Rico Police Bureau, is a law enforcement agency with jurisdiction over the entire Commonwealth of Puerto Rico. It is a division of the Puerto Rico Department ...
Memorial Monument and
The Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; a ...
Memorial Monument. The ''Loma de los Vientos'', or ''Loma del Viento'' (Spanish for "hill of winds"), is a small open green area located northwest of the Capitol, next to
Castle San Cristóbal, and it often hosts events such as the
Epiphany
Epiphany may refer to:
* Epiphany (feeling), an experience of sudden and striking insight
Religion
* Epiphany (holiday), a Christian holiday celebrating the revelation of God the Son as a human being in Jesus Christ
** Epiphany season, or Epiph ...
celebrations.
Luis Muñoz Rivera Park
The Luis Muñoz Rivera Park (or Parque Luis Muñoz Rivera in Spanish) is a 27.2 acre (110,000 m2) recreational public space located in Puerta de Tierra in San Juan, Puerto Rico. The park was named in honor of Puerto Rican statesman Luis Muñoz ...
is a 27.2 acre recreational and historic park located in
Puerta de Tierra
Puerta de Tierra is a ''subbarrio'' (subdistrict) occupying the eastern portion of the Islet of San Juan and the ''barrio'' of San Juan Antiguo in the municipality of San Juan, Puerto Rico. The name Puerta de Tierra (Spanish for ''land gate'') ...
, between Luis Muñoz Rivera,
Ponce de León
Ponce may refer to:
*Ponce (surname)
*
*Ponce, Puerto Rico, a city in Puerto Rico
** Ponce High School
** Ponce massacre, 1937
* USS ''Ponce'', several ships of the US Navy
*Manuel Ponce, a Mexican composer active in the 20th century
* British sla ...
and Constitución avenues. It is the largest public square in Puerto Rico, and it is home to several historic sites such as the
Polvorín San Gerónimo de Boquerón, which used to supply gunpowder to the nearby
Fortín de San Gerónimo
Fortín de San Gerónimo de Boquerón is a small fort located at the mouth of the Condado Lagoon, across from the historic sector of Miramar in San Juan, Puerto Rico.
It was built during the 18th century to replace a smaller battery (called E ...
. The park used to host a small zoo, and currently hosts gazebos, gardens, restaurants and access to the beach. The park has been listed on the
National Register of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic v ...
since November 14, 2007.
The
Polvorin de Miraflores is a historic district and park located next to the
Puerto Rico Convention Center
The Dr. Pedro Rosselló González Puerto Rico Convention Center (PRCC) (or ''Centro de Convenciones de Puerto Rico Dr. Pedro Rosselló González'' in Spanish), or simply Puerto Rico Convention Center, is a convention center located in Isla Gr ...
in
Isla Grande
Isla Grande is a small island and Corregimientos of Panama, corregimiento in Portobelo District, Colón Province, Panama, off the Caribbean coast. It had a population of 1,037 . Its population as of 1990 was 626; its population as of 2000 was 1,05 ...
,
Santurce. The ammunition storage house dates to the mid-18th century and it is also listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
Another historic district currently under revitalization is the
San Juan Waterworks historic district which contains the Old Piedras River Aqueduct. There are plans to revitalize the old aqueduct structures and its surroundings to create a historic park open to visitors and researchers.

Municipal parks
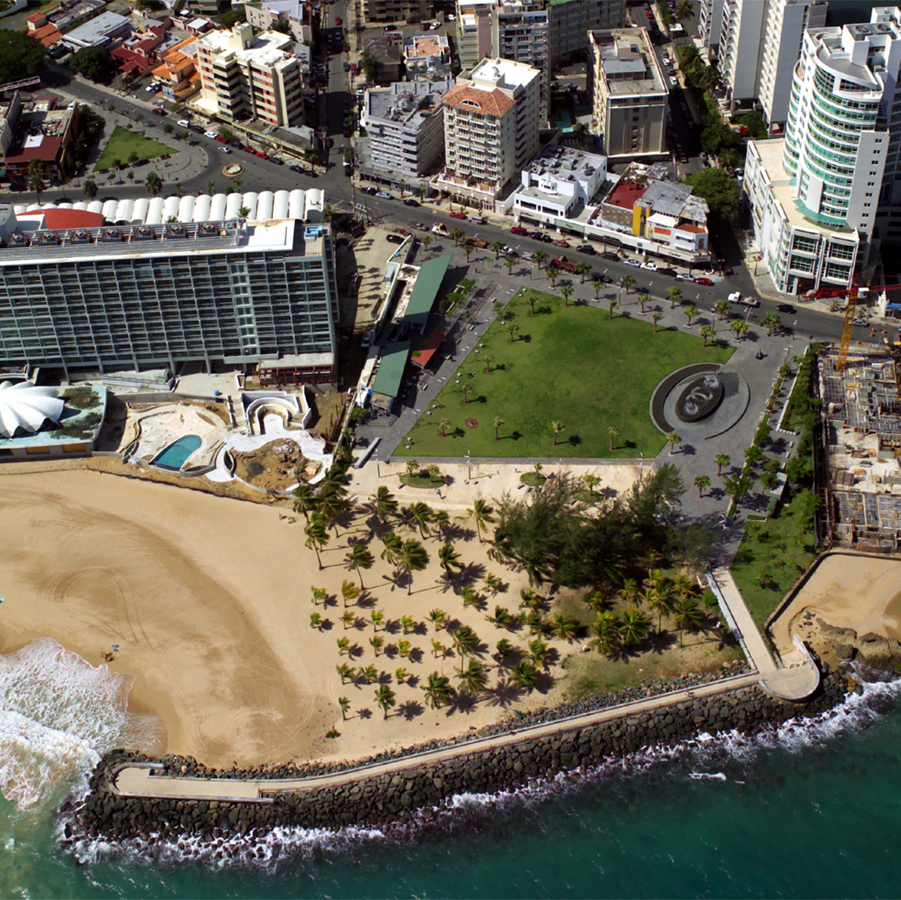

Some of the recreational parks of the municipality include
Bahía Urbana, a waterfront park located in Old San Juan and Puerta de Tierra by the San Juan Bay; the
Paseo de Puerta de Tierra, a recreational walkway along the Atlantic Ocean cliffs of Puerta de Tierra that connects the Puerto Rico Capitol with
El Escambrón Beach
El Escambrón Beach (Spanish: ''Balneario del Escambrón'') is a public-access beach located in the San Juan Antiguo sub-district (''subbarrio'') of Puerta de Tierra, next to the Luis Muñoz Rivera Park in San Juan, Puerto Rico. The beach and rec ...
and Luis Muñoz Rivera Park.
Ventana al Mar,
Laguna del Condado Jaime Benítez Park, Parque del Indio are some of the parks located in
El Condado
Condado is an oceanfront, tree-lined, pedestrian-oriented upper middle to upper class community in Santurce. It is one of the forty subbarrios of Santurce in San Juan, Puerto Rico.
Setting
Condado is an upscale neighborhood located on the bea ...
district of Santurce. Dr. José Celso Barbosa Park is located in
Ocean Park, also in Santurce.
Parque Central, also known as the San Juan Municipal Central Park, is a large park and recreational complex located in southern Santurce near the mouth of the
Puerto Nuevo River
The Río Puerto Nuevo is a river of Puerto Rico.
Flood control project
In mid 2018, the United States Army Corps of Engineers announced it would be undertaking a major flood control project of the river, with a budget of $1552.4 million.
See ...
and the
Martín Peña Channel
The Martín Peña Channel (Spanish: ''Caño de Martín Peña'') is a body of water in San Juan, Puerto Rico. The similarly named Martín Peña is a neighbourhood, with informal housing, adjacent to the channel.
The channel runs from San Juan B ...
. The Enrique Martí Coll Linear Park connects the Central Park to
Hato Rey
Hato Rey is a former barrio located in the northwest part of the dissolved municipality of Río Piedras. It now stretches over three barrios, of the municipality of San Juan, Puerto Rico:
Urban landscape
Its name means "king's cattle farm" (' ...
through the
Caño Martín Peña Nature Reserve.
Luis Muñoz Marín Park, La Merced Park, Dr. José N. Gándara Park, Santiago Iglesias Pantín Park are some of the parks located in Hato Rey. Luis Muñoz Marín Park is one of the largest in the municipality. It is located in the
Gobernador Piñero district between Hato Rey and
Puerto Nuevo. The park has gazebos that can be rented for events, green areas for strolls, biking and picnics, an artificial lake with paddleboats for rent ($6), and a number of playgrounds for children. Its main attraction is the
cableway
Cable transport is a broad class of transport modes that have cables. They transport passengers and goods, often in vehicles called cable cars. The cable may be driven or passive, and items may be moved by pulling, sliding, sailing, or by driv ...
that crosses the park and offers scenic views of the
Piedras River and the city while providing transportation to the
Roberto Clemente Coliseum
Roberto Clemente Coliseum ( Spanish: ''Coliseo Roberto Clemente'') is a sports and concert arena located in San Juan, Puerto Rico. It was, for many years, Puerto Rico's largest indoor event facility, and remains one of the largest.
General info ...
and the
Hiram Bithorn Stadium
Hiram Bithorn Stadium (Spanish: Estadio Hiram Bithorn) is a baseball park in San Juan, Puerto Rico, built in 1962 and designed by Puerto Rican architect Pedro Miranda. It is operated by the municipal government of the city of San Juan. Its name ho ...
.
Nature reserves
The municipality of San Juan is home to various important ecosystems and preserved natural areas. Some of the ecosystems of the
San Juan Bay National Estuary, which is the only tropical estuary in the
National Estuary Program
In the United States, the National Estuary Program (NEP) provides grants to states where governors have identified nationally significant estuaries that are threatened by pollution, land development, or overuse. Governors have identified a total o ...
network, are protected by numerous nature reserves and protected areas such as the
Caño Martín Peña Nature Reserve. Other areas protected under the San Juan Bay National Estuary include
El Condado Lagoon, the
San José Lagoon and
El Boquerón where the San Antonio Creek and the Condado Lagoon connect with the Atlantic Ocean.
Two of the 20
state forests
A state forest or national forest is a forest that is administered or protected by some agency of a sovereign state, sovereign or federated state, or territory (country subdivision), territory.
Background
The precise application of the terms va ...
of Puerto Rico are located in the municipality of San Juan: the
New Millennium Urban Forest, which is also part of the San Juan Ecological Corridor, and the
San Patricio Urban Forest, a
secondary forest located next to a
mogote
A mogote () is a generally-isolated steep-sided residual hill in the tropics composed of either limestone, marble, or dolomite. Mogotes are surrounded by nearly flat alluvial plains. The hills typically have a rounded, tower-like form.
Overvi ...
. The Hermanas Sendra and San Juan Park Protected Natural Areas are located inland within the municipality of San Juan in the barrios of
Caimito and
Cupey.
Cityscape
Architecture
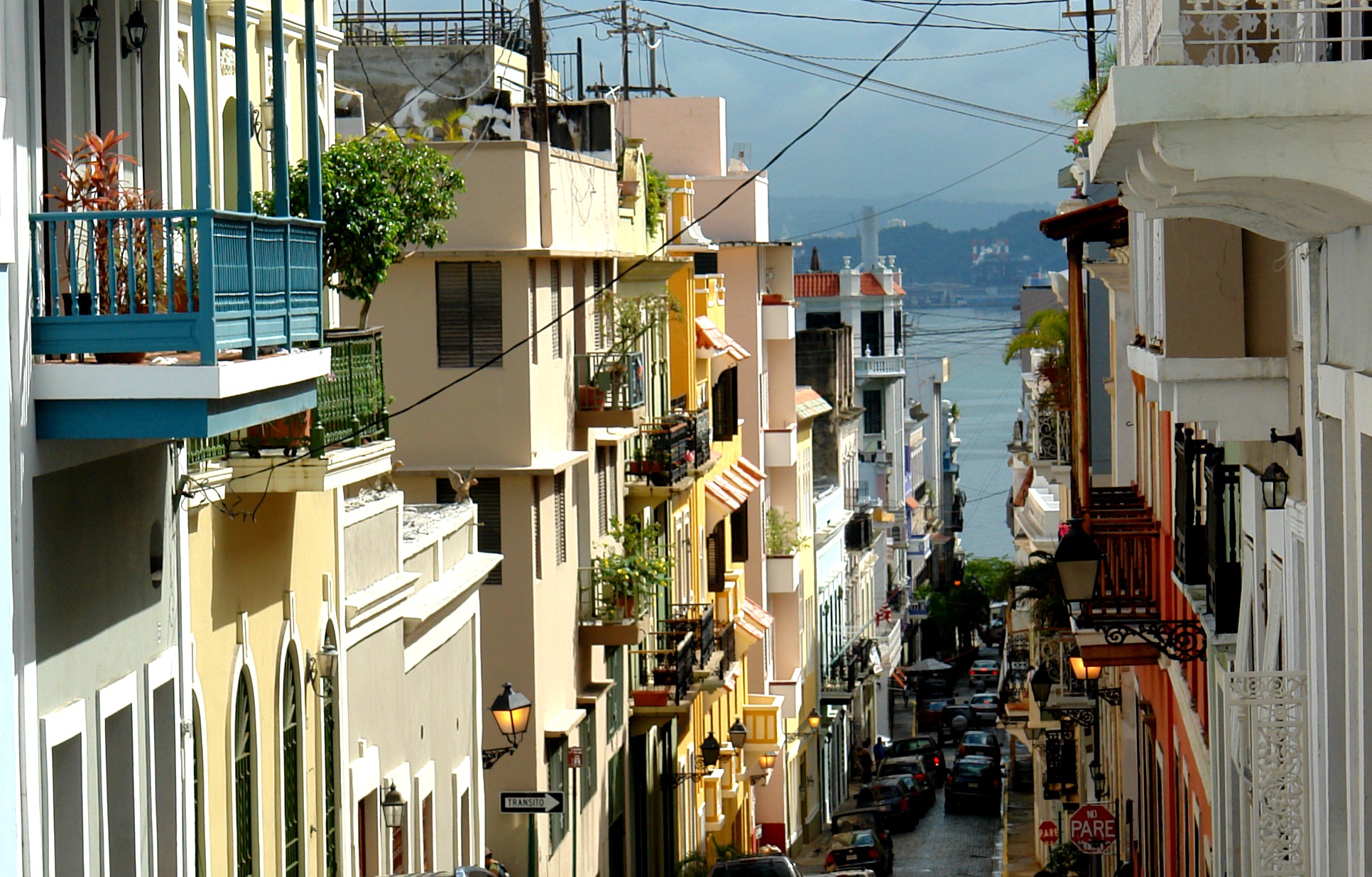


The architecture of San Juan is very diverse, due to its size and all the cultural influences received during its existence. The oldest part of the city, known as
Old San Juan
Old San Juan ( es, Viejo San Juan) is a historic district located at the "northwest triangle" of the islet of San Juan. Its area roughly correlates to the Ballajá, Catedral, Marina, Mercado, San Cristóbal, and San Francisco sub-barrios (s ...
, mostly features the influence of
Spanish architecture
Spanish architecture refers to architecture in any area of what is now Spain, and by Spanish architects worldwide. The term includes buildings which were constructed within the current borders of Spain prior to its existence as a nation, when ...
. This part of the city is comprised by a network of
"setted" roads usually surrounded by colonial, two-storied houses built on
masonry
Masonry is the building of structures from individual units, which are often laid in and bound together by mortar; the term ''masonry'' can also refer to the units themselves. The common materials of masonry construction are bricks, building ...
. Some colonial structures have been restored and serve either as government offices or museums.
Some examples are the
Ballajá Barracks
The Ballajá Barracks (''Cuartel de Ballajá'' in Spanish) is a historic building and former military barracks located in the Ballajá section of Old San Juan, in the city of San Juan, Puerto Rico. It is located close to El Morro and its esplana ...
, which now serve as museum and headquarters of several cultural organizations;
La Fortaleza
La Fortaleza (lit., "The Fortress" ) is the official residence of the governor of Puerto Rico. It was built between 1533 and 1540 to defend the harbor of San Juan. The structure is also known as Palacio de Santa Catalina (Saint Catherine's Palac ...
, which has served as the residence of the
Governor of Puerto Rico
The governor of Puerto Rico ( es, gobernador de Puerto Rico) is the head of government of the Commonwealth (U.S. insular area), Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, and commander-in-chief of the Puerto Rico National Guard.
The governor has a duty ...
since the 16th Century; and the Ancient Welfare Asylum, which now houses the Institute of Puerto Rican Culture, among others. Old San Juan also features several public squares, like the
Plaza de Armas
The ''Plaza de Armas'' (literally Weapons Square, but better translated as Parade Square or parade ground) is the name for Latin American main squares. In the central region of Mexico this space is known as El Zócalo and in Central America as ...
, located in front of San Juan City Hall; and cathedrals, like the
Cathedral of San Juan Bautista.
Old San Juan is also notable for being partly enclosed by
massive walls and fortifications built by the
Spanish government
gl, Goberno de España eu, Espainiako Gobernua
, image =
, caption = Logo of the Government of Spain
, headerstyle = background-color: #efefef
, label1 = Role
, data1 = Executive power
, label2 = Established
, da ...
.
The architecture is more varied in other districts of the city, and the different
Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
,
American
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, pe ...
and
Puerto Rican construction styles that reflect the historic architecture trends are most evident in the districts of
Puerta de Tierra
Puerta de Tierra is a ''subbarrio'' (subdistrict) occupying the eastern portion of the Islet of San Juan and the ''barrio'' of San Juan Antiguo in the municipality of San Juan, Puerto Rico. The name Puerta de Tierra (Spanish for ''land gate'') ...
,
Santurce,
Hato Rey
Hato Rey is a former barrio located in the northwest part of the dissolved municipality of Río Piedras. It now stretches over three barrios, of the municipality of San Juan, Puerto Rico:
Urban landscape
Its name means "king's cattle farm" (' ...
and
downtown Río Piedras, with
Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
,
Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ...
, Art Deco, and Mid-century modern, Mid-Century Modern being the most popular styles. Many of the buildings that best exemplify these architectural trends in San Juan are also inscribed in the United States National Register of Historic Places listings, United States National Register of Historic Places (NRHP), such as the Nuestra Señora de Lourdes Chapel (Gothic Revival architecture, Gothic Revival, 1907), the Antiguo Casino de Puerto Rico (Beaux-Arts architecture, Beaux-Arts, 1917),
[ and ] the Normandie Hotel (Art Deco, 1942),
and the Supreme Court Building (Puerto Rico), Puerto Rico Supreme Court Building (Modern architecture, Modern, 1955).
[ and ] The University of Puerto Rico, Río Piedras Campus is also home to a rich variety of buildings that showcase the history of Puerto Rican architecture throughout the past 120 years, with buildings designed by notable architects such as Frank Lloyd Wright's student Henry Klumb, Edward H. Bennett, William E. Parsons, and Rafael Carmoega who designed the distinctive Roosevelt Tower, clock tower and the The Quadrangle (University of Puerto Rico, Río Piedras), university quadrangle, both of which were inscribed in the NRHP in 1984.
Barrios
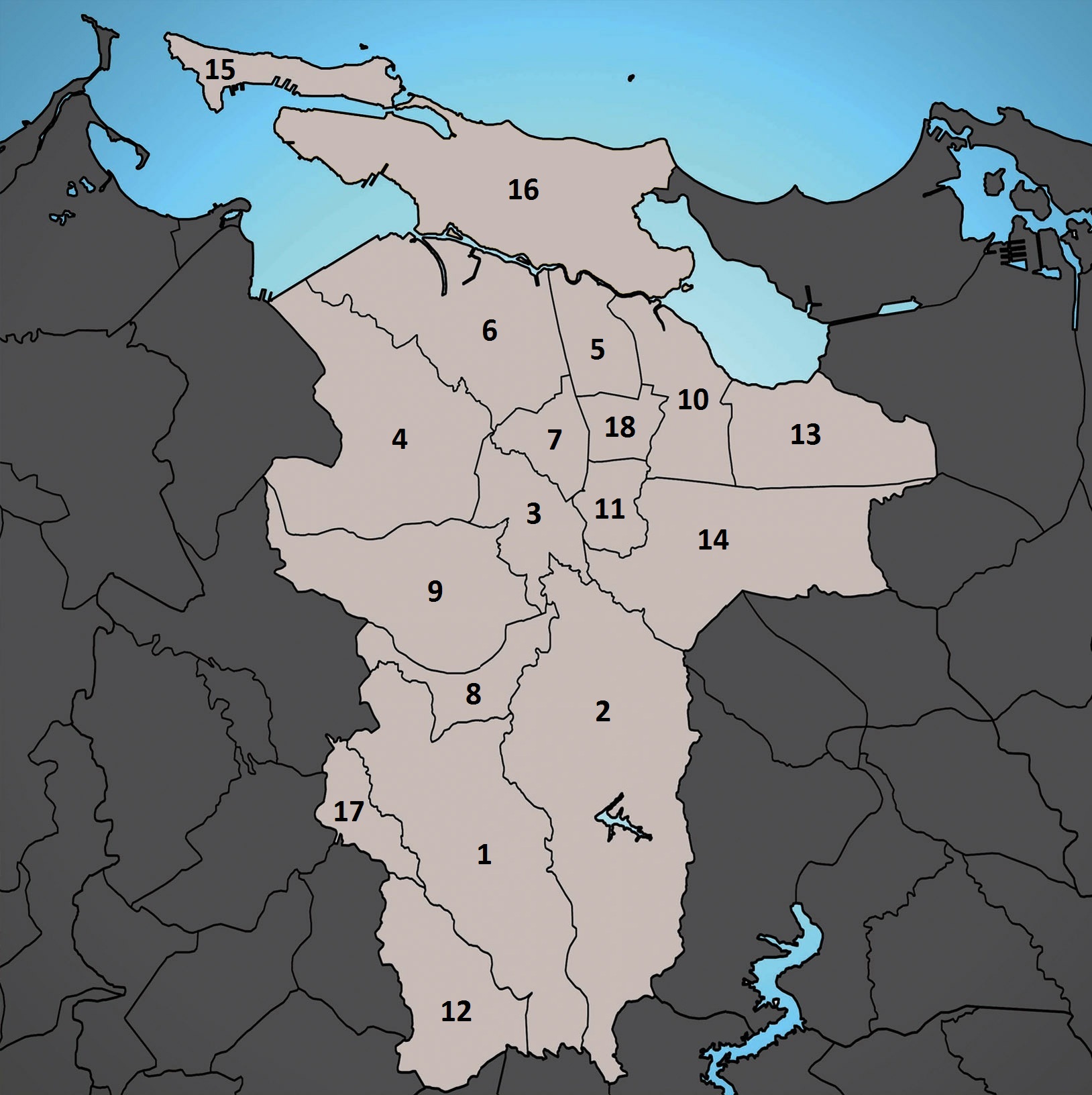
As with the other Puerto Rican municipalities, San Juan is administratively divided into ''Barrios of Puerto Rico, barrios.'' What is now known as
Old San Juan
Old San Juan ( es, Viejo San Juan) is a historic district located at the "northwest triangle" of the islet of San Juan. Its area roughly correlates to the Ballajá, Catedral, Marina, Mercado, San Cristóbal, and San Francisco sub-barrios (s ...
occupied the western end of a rocky islet, the Isleta de San Juan, at the mouth of San Juan Bay. During the 20th century, the main population centers surged well beyond the walls of the old city and onto Puerto Rico's main island and merged with the existing settlements east and south of Old San Juan. Together with
Puerta de Tierra
Puerta de Tierra is a ''subbarrio'' (subdistrict) occupying the eastern portion of the Islet of San Juan and the ''barrio'' of San Juan Antiguo in the municipality of San Juan, Puerto Rico. The name Puerta de Tierra (Spanish for ''land gate'') ...
, Old San Juan comprises the barrio of San Juan Antiguo.
With the annexation of Río Piedras, Puerto Rico, Río Piedras in 1951, the municipality of San Juan grew to four times its previous size. As a result, the municipality also went from 2 to 18 barrios (barrios), 16 of which fall within the former municipality of Río Piedras. Eight of the 18 barrios are further subdivided into subbarrios, including the two barrios (San Juan Antiguo and
Santurce) that belonged to the original municipality of San Juan.
The 18 barrios are:
#
Caimito
#
Cupey
# El Cinco, San Juan, Puerto Rico, El Cinco
#
Gobernador Piñero
# Hato Rey Central, San Juan, Puerto Rico, Hato Rey Central
# Hato Rey Norte, San Juan, Hato Rey Norte
# Hato Rey Sur, San Juan, Puerto Rico, Hato Rey Sur
# Monacillo, San Juan, Puerto Rico, Monacillo
# Monacillo Urbano, San Juan, Puerto Rico, Monacillo Urbano
# Oriente, San Juan, Puerto Rico, Oriente
# Pueblo, San Juan, Puerto Rico, Pueblo
# Quebrada Arenas, San Juan, Puerto Rico, Quebrada Arenas
# Sabana Llana Norte, San Juan, Puerto Rico, Sabana Llana Norte
#
Sabana Llana Sur
# San Juan Antiguo (not to be confused with Old San Juan, Puerto Rico, Old San Juan, a historic district with some overlapping areas)
#
Santurce
# Tortugo, San Juan, Puerto Rico, Tortugo
# Universidad, San Juan, Puerto Rico, Universidad
San Juan Antiguo
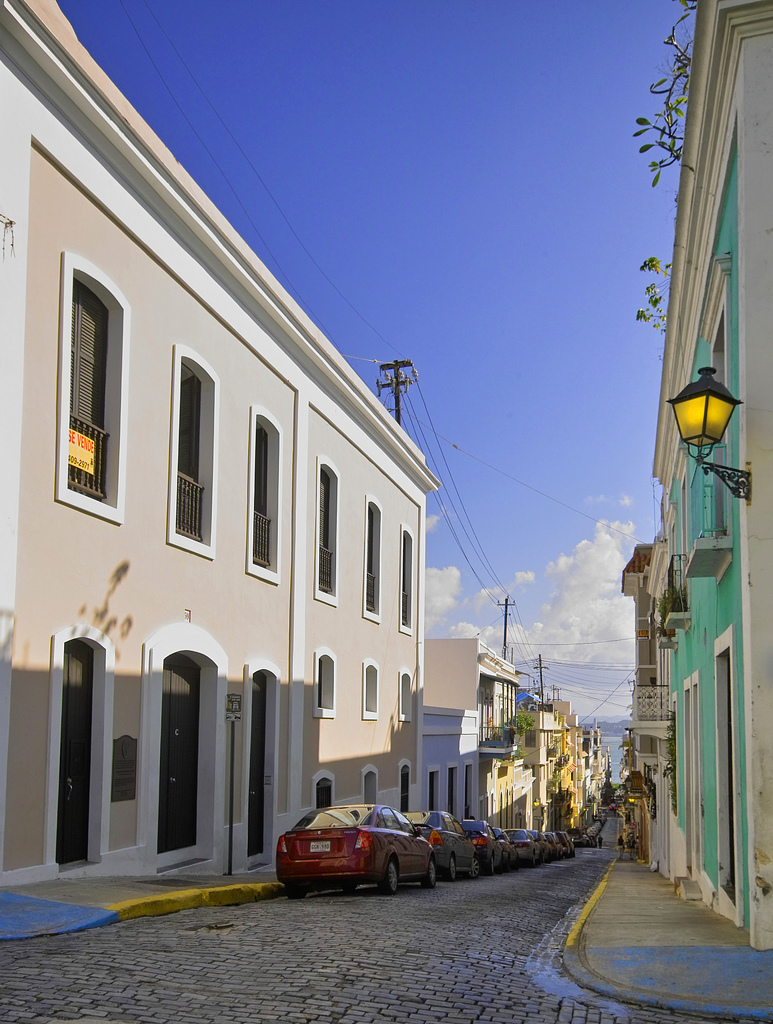


During the Spanish colonial times most of the urban population resided in what is today known as
Old San Juan
Old San Juan ( es, Viejo San Juan) is a historic district located at the "northwest triangle" of the islet of San Juan. Its area roughly correlates to the Ballajá, Catedral, Marina, Mercado, San Cristóbal, and San Francisco sub-barrios (s ...
. This sector is located on the western half of a small island called the Isleta de San Juan, which is connected to the mainland by two bridges and a causeway. The small island, which comprises an area of , also hosts the working-class neighborhood of Puerta de Tierra and most of Puerto Rico's Executive Departments of the Government of Puerto Rico, central government buildings, including the Puerto Rico Capitol, Commonwealth's Capitol. This is also the largest and most populated ''subbarrio'' of San Juan Antiguo.
The main central part of the old city is characterized by narrow streets made of blue cobblestone and picturesque colonial buildings, some of which date back to the 16th and 17th century. Sections of the old city are surrounded by massive walls and several defensive structures and notable forts. These include the 16th-century
Fort San Felipe del Morro
Castillo San Felipe del Morro, also known as El Morro, is a citadel built between 16th and 18th centuries in San Juan, Puerto Rico.[ww ...](_blank)
and the 17th-century
Fort San Cristóbal, both part of
San Juan National Historic Site, and the 16th-century La Fortaleza, El Palacio de Santa Catalina, also known as
La Fortaleza
La Fortaleza (lit., "The Fortress" ) is the official residence of the governor of Puerto Rico. It was built between 1533 and 1540 to defend the harbor of San Juan. The structure is also known as Palacio de Santa Catalina (Saint Catherine's Palac ...
, which serves as the governor's mansion.
Other buildings of interest predating the 20th century are the ''Ayuntamiento or Alcaldía'' (San Juan City Hall), the ''Diputación Provincial'' and the ''Real Intendencia'' buildings, which house the Puerto Rico Department of State, the Casa Rosa, the San José Church (1523) and the adjacent Hotel El Convento, the former house of the Ponce de León family known as Casa Blanca (San Juan), Casa Blanca, the Teatro Tapia, the former Spanish barracks (now Ballajá Barracks, Museum of Ballajá), ''La Princesa'' (former municipal jail, now headquartering the Puerto Rico Tourism Company), and the Santa María Magdalena de Pazzis Cemetery, located just outside the city walls. The
Cathedral of San Juan Bautista (construction began in the 1520s) is also located in Old San Juan and contains the tomb of the Spanish explorer and settlement founder
Juan Ponce de León. Old San Juan, also known as the "old city", is the main cultural tourist attraction in Puerto Rico; its bayside is lined by dock slips for large cruise ships.
Santurce

Santurce is the largest and most populated barrio in the municipality of San Juan, and one of the most densely populated areas of the island (13,257.4 persons per square mile). Santurce, originally named ''San Mateo de Cangrejos'' (Saint Matthew of the Crabs), was a settlement for Freedman, freed African slaves during the early days of the city. After Pablo Ubarri Capetillo, a Spanish railroad developer and ''Count of San José de Santurce'' under the Spanish colonial period, sought permission to link San Juan with Río Piedras proper via steam tramway in 1878, the time it took to travel between both points were shortened and thereby stimulated the colonization and growth of the district. At the beginning of the twentieth century an electric trolley was installed, the township was split into three parts, and its main settlement, merged with the city, was renamed using the Spanish spelling of Santurtzi (''Saint George'' in Basque), Ubarri's birthplace in Biscay, Vizcaya, Spain. The "Museo de Arte de Puerto Rico" (Puerto Rico Museum of Art) and other important cultural venues are located in Santurce.
This barrio is further divided into subbarrios such as the tourist-oriented neighborhood of Condado (Santurce), Condado, which occupies land that used to be owned by Ubarri Capetillo. Beaches such as nearby
Ocean Park, popular with swimmers, surfers and kitesurfers, are found all along the district's Atlantic coastline which is also the locus of numerous hotels. Miramar (Santurce), Miramar is mainly a residential area rising south of the Condado Lagoon. It comprises the former ''barrio'' of Miraflores, as well as drained marshland and landfill over which was built San Juan's first airport, the Isla Grande airport, which was renamed Fernando Luis Ribas Dominicci Airport in honor of Major Fernando Luis Ribas-Dominicci (USAF). Miramar now hosts the
Puerto Rico Convention Center
The Dr. Pedro Rosselló González Puerto Rico Convention Center (PRCC) (or ''Centro de Convenciones de Puerto Rico Dr. Pedro Rosselló González'' in Spanish), or simply Puerto Rico Convention Center, is a convention center located in Isla Gr ...
as well as some of San Juan Harbor's cruise ship piers. In 2005 Miramar was designated an historical district of Puerto Rico.
Río Piedras

South of Santurce is
Hato Rey
Hato Rey is a former barrio located in the northwest part of the dissolved municipality of Río Piedras. It now stretches over three barrios, of the municipality of San Juan, Puerto Rico:
Urban landscape
Its name means "king's cattle farm" (' ...
, part of the former municipality of Río Piedras. Hato Rey was grazing ground for cattle owned by the royal government (hence its name, the ''King's Herd'' in Spanish) as early as the 16th century,
and is now considered the financial center of the island. A section of this district is often referred to as ''Milla de Oro'' (actually long) due in part to the many banks and businesses located there.
In the southern part of the city is the socially diversified community of Río Piedras. Founded in the mid-1850s, Río Piedras was a separate town which hosted sugar cane plantations and the estates of some of San Juan's wealthiest inhabitants (as well as their working-class staff). The Spanish colonial governors also had their summer home there on land which eventually gave way to the main campus of the
University of Puerto Rico
The University of Puerto Rico ( es, Universidad de Puerto Rico, UPR) is the main public university system in the U.S. Commonwealth of Puerto Rico. It is a government-owned corporation with 11 campuses and approximately 58,000 students and 5,3 ...
. In 1951 the municipalities of San Juan and Río Piedras were merged to redefine San Juan's current city limits. Today Río Piedras comprises the largest area of the municipality of San Juan. and is home to the "Plaza del Mercado" (Río Piedras Marketplace), the main campus and the Medical Sciences campus of the
University of Puerto Rico
The University of Puerto Rico ( es, Universidad de Puerto Rico, UPR) is the main public university system in the U.S. Commonwealth of Puerto Rico. It is a government-owned corporation with 11 campuses and approximately 58,000 students and 5,3 ...
and the
San Juan Botanical Garden
The San Juan Botanical Garden, officially known as the Botanical Garden of the University of Puerto Rico, is located in the Caribbean city of San Juan, capital of Puerto Rico. This lush “urban garden” of native and exotic flora serves a ...
.
Demographics
The municipality of San Juan has a population of 342,259 as of the 2020 US Census, making it the Municipalities of Puerto Rico, largest in Puerto Rico,
and the List of United States cities by population, 57th largest in the United States and its territories.
From 1899 to 1950 the municipality of San Juan excluded the township of Río Piedras. For this reason, population data and land area for the period make reference only to the Antiguo San Juan and Santurce ''barrios'', or subdivisions, of San Juan. The old municipality of Río Piedras constituted the third most populated city of Puerto Rico at the time of its annexation in 1951. Its strategic location south of the capital served as a junction for all the principal ways of transportation of the island and as a geographical entry to San Juan, which are factors that prompted Río Piedras's dramatic urban development in the 20th century.
According to the 2010 United States Census, 2010 Census, the racial composition of San Juan was as follows:
* White American, White: 68.0% (Non-Hispanic Whites: 1.2%)
* Black or African American: 18.3% (Non-Hispanic Blacks: 0.3%)
* Native Americans in the United States, American Indian: 0.8%
* Asian American, Asian: 0.4%
* Native Hawaiians, Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander American, Pacific Islander: 0.0%
* Some other race: 8.2%
* Multiracial American, Two or more races: 4.0%
* Hispanic and Latino Americans, Hispanic or Latino (of any race): 98.2%
Among the Hispanic and Latino population, Puerto Rican people, Puerto Ricans are the largest group; they make up 87.5% of San Juan's Hispanic population. People of Dominican American, Dominican descent make up 7.6% of the Hispanic population, while those of Cuban American, Cuban descent form 1.7% of the Hispanic populace. Other Hispanic and Latino groups collectively form 3.2% of San Juan's Hispanic population.
There are 4,822 whites and 1,187 blacks of non-Hispanic origin living in San Juan. Non-Hispanic whites and blacks form 1.2% and 0.3% of San Juan's population respectively. There are also approximately 673 Asians of non-Hispanic origin in San Juan; they make up less than 0.1% of the population. However, Asians of Hispanic and non-Hispanic origin together number at 6,342.
The vast majority of Asians in San Juan are of Chinese American, Chinese descent; of the 6,342 Asians, 4,928 are Chinese. Chinese comprise 1.4% of the population. The only other sizable Asian group in San Juan are Indian Americans; there are 698 people of Indian descent in the city, forming 0.2% of the population. There are very small numbers of people of Filipino American, Filipino, Japanese American, Japanese, and Vietnamese American, Vietnamese ancestry; none of these groups number more than 100 members.
According to the 2006–2008 American Community Survey, 87.5% of San Juan's population was native and 12.5% were foreign-born. Of the native population, 86.9% were born in Puerto Rico or the U.S. proper, of which 75.6% were born in Puerto Rico and 8.9% were born in the U.S. The other 0.7% were born in a different U.S. territory or born abroad to American parents. The remaining 11.9% of the population were born outside the United States and U.S. territories.
In recent years, an increasing number of Americans not of Hispanic ancestry (both of African American and of White American descent) have moved to San Juan. In addition, a large number of Stateside Puerto Ricans have settled in the city upon their return to Puerto Rico. There is also a growing West Indian population, both of Hispanic and non-Hispanic origin.
San Juan today is home to the largest History of the Jews in Puerto Rico, Jewish community in Puerto Rico, and one of the largest Jewish communities in the Caribbean, with more than 2,000 people attending two local synagogues in
Santurce (the Conservative Judaism, Conservative Shaare Zedeck Synagogue and the Reform Judaism, Reform Temple Beth Shalom) and an additional synagogue (the Chabad affiliated organizations, Chabad Jewish Center of Puerto Rico) in Isla Verde, Puerto Rico, Isla Verde in neighboring
Carolina.
In terms of ancestry, 23,875 people claimed American ancestry, which is equivalent to 5.8% of San Juan's population. Other sizable ancestry groups included those of Italian American, Italian descent, French American, French descent, and West Indian descent. People of Italian descent numbered at 1,694, forming 0.4% of the population; people of French descent numbered at 1,064, forming 0.2% of the population. Finally, those of West Indian descent numbered at 1,393, forming 0.3% of San Juan's population. Approximately 1,026 people claimed Sub-Saharan African ancestry; 719 claimed Irish American, Irish ancestry; 646 claimed German American, German ancestry; 431 claimed Arab American, Arab ancestry, and 346 claimed English American, English ancestry. There are many other ancestry groups in San Juan, but they are very scant.
Economy

San Juan experienced significant economic growth following World War II. During this period the city underwent an industrial revolution, although as of 1984 it had never generated its own economic region.
[Microsoft Encarta Biblioteca (2006), Microsoft Corporation] The city's economy relies mostly on companies dedicated to the manufacture of several products, including: chemical substances (bleach and house cleaning products); pharmaceuticals; rum and other beverages; fertilizers; electric tools; Electronics, electronic devices; plastics, textiles, and food-based products.
Tourism is also a key industry, based on San Juan's proximity to Puerto Rico's main airport, the Luis Muñoz Marín International Airport.
The tourism focus of the city is located in the district of Condado Beach where there are luxurious hotels.
Historical locations such as El Morro, Old San Juan and El Cuartel de Ballaja are promoted in tourism campaigns. The district of Hato Rey contains a corporate sector known as Milla de Oro (Golden Mile) which serves as the headquarters of local and international banks. San Juan's Hato Rey district is often referred to as the "Wall Street of the Caribbean", due to the influence of the area on Puerto Rico and the Caribbean's economy.
San Juan is also home to the Popular, Inc., parent company of Banco Popular de Puerto Rico, Popular Bank, E-Loan, and a Fortune 1000 company as of 2022. Other companies based in San Juan include ATH (interbank network), ATH Network, First BanCorp, Liberty Puerto Rico, The Cervantes Group, and Triple-S Management Corporation. Seaborne Airlines is headquartered on the ninth floor of the World Plaza Building in Hato Rey.
Tourism


Technological advances after World War II in the development of the airliner, coupled with the island's climate and natural setting, have transformed San Juan into the springboard for tourism around the island, and has made the rest of the Caribbean known throughout the world during the last fifty years. Today the capital features hotels, museums, historical buildings, restaurants, parks, beaches and shopping centers.
Old San Juan is often emphasized in tourism campaigns, promoting the historic nature of its colonial buildings and narrow streets covered by cobblestones, a blue stone cast from furnace slag; they were brought over as ballast on Spanish ships.
This includes the city's ancient defensive wall and forts, most notably
El Morro and the Castillo San Cristóbal (San Juan), Castillo San Cristóbal.
On January 23, 1984, both of these edifices together with
La Fortaleza
La Fortaleza (lit., "The Fortress" ) is the official residence of the governor of Puerto Rico. It was built between 1533 and 1540 to defend the harbor of San Juan. The structure is also known as Palacio de Santa Catalina (Saint Catherine's Palac ...
and Fortín San Juan de la Cruz, El Cañuelo (in nearby
Toa Baja
Toa Baja (, ) is a town and municipality of Puerto Rico located in the northern coast, north of Toa Alta and Bayamón; east of Dorado; and west of Cataño. Toa Baja is spread over five barrios, including Toa Baja Pueblo (the downtown area and ...
) were included as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, catalogued as being part of humanity's cultural patrimony as part of the
National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an agency of the United States federal government within the U.S. Department of the Interior that manages all national parks, most national monuments, and other natural, historical, and recreational propertie ...
-administered
San Juan National Historic Site. The restaurants and art galleries in the zone are visited by tourists and locals alike.

Outside of Old San Juan, the Puerto Rico Convention Center District (PRCC) includes the
Puerto Rico Convention Center
The Dr. Pedro Rosselló González Puerto Rico Convention Center (PRCC) (or ''Centro de Convenciones de Puerto Rico Dr. Pedro Rosselló González'' in Spanish), or simply Puerto Rico Convention Center, is a convention center located in Isla Gr ...
, which hosts a number of local and international events throughout the year such as the Puerto Rico Comic Con, the biggest of its kind in the Caribbean. The Distrito T-Mobile, PRCC District also hosts a number of hotels, nightclubs, shops, cinemas, bars and restaurants, the Coca-Cola Music Hall, and the Toro Verde Eco Adventure Park.
Other notable tourist attractions in San Juan include the Condado Beach, Condado and
Ocean Park Beaches, El Escambrón Beach, El Escambrón and the
Fortín de San Gerónimo
Fortín de San Gerónimo de Boquerón is a small fort located at the mouth of the Condado Lagoon, across from the historic sector of Miramar in San Juan, Puerto Rico.
It was built during the 18th century to replace a smaller battery (called E ...
, La Placita de Santurce, the Luis A. Ferré Performing Arts Center, the Luis Muñoz Marín Park, Luis Muñoz Marín and
Luis Muñoz Rivera Park
The Luis Muñoz Rivera Park (or Parque Luis Muñoz Rivera in Spanish) is a 27.2 acre (110,000 m2) recreational public space located in Puerta de Tierra in San Juan, Puerto Rico. The park was named in honor of Puerto Rican statesman Luis Muñoz ...
s, Plaza Las Américas and The Mall of San Juan, the Museum of Art of Puerto Rico, the Puerto Rico Museum of Contemporary Art, the Museo de Vida Silvestre, San Juan Wildlife Museum, and the San Juan Botanical Garden, University of Puerto Rico Botanical Garden, among others. The University of Puerto Rico's main campus in Río Piedras is also of interest with its The Quadrangle (University of Puerto Rico, Río Piedras), historic quadrangle and Roosevelt Tower, clock tower, its number of theaters and venues which host events such as the Casals Festivals, and a museum. San Juan is also used by tourists as a base to explore other attractions within and outside the San Juan metropolitan area, such as the Bacardi Cathedral of Rum and Cataño barrio-pueblo, boardwalk in
Cataño, the "Pork Highway" of Guavate, Cayey, Puerto Rico, Guavate in Cayey, Puerto Rico, Cayey, the bioluminiscent bay in Fajardo, Puerto Rico, Fajardo, the beaches and street food of Piñones (Loíza, Puerto Rico), Piñones in Loíza, Puerto Rico, Loíza, and El Yunque National Forest recreational areas in the municipalities of Luquillo, Puerto Rico, Luquillo and Río Grande, Puerto Rico, Río Grande.
Post Hurricane Maria
An April 2019 report indicated that, by that time, repairs after Hurricane Maria were moving rapidly. Only a few hotels were still closed in San Juan and that life for tourists in and around the capital had, for the most part, returned to normal. By October 2019, nearly all of the popular amenities for tourists, in the major destinations such as San Juan, Ponce and Arecibo, were in operation on the island and tourism was rebounding. This was important for the economy, since tourism provides up 10% of Puerto Rico's GDP, according to Discover Puerto Rico.
In late November 2019, reports indicated that 90 calls to San Juan by Royal Caribbean Cruises Ltd., Royal Caribbean ships would be cancelled during 2020 and 2021. This step would mean 360,000 fewer visitors, with a loss to the island's economy of $44 million. As well, 30 ship departures from San Juan were being canceled.
Arts and culture

San Juan is the birthplace of artists and musicians who have significantly influenced Puerto Rican culture. During the 20th century, the musical aspect of the city was influenced by performers including West Indian Americans, Afro-Caribbean dancer and choreographer Sylvia del Villard and José Enrique Pedreira who became a composer of Puerto Rican Music of Puerto Rico#Danza, ''Danzas''. International musicians such as opera singer Justino Díaz and Grammy Award winners Daddy Yankee, Ramón Ayala (Daddy Yankee) and Ricky Martin were born in the city. Other notable residents include writers Giannina Braschi and Tomás Blanco (writer), Tomas Blanco, award-winning actors Raul Julia and Benicio del Toro, and comedian José Miguel Agrelot. Rafael Cordero (educator), Rafael Cordero (1790–1868), was influential in the development of Puerto Rican education and has been once renowned as "The Father of Public Education in Puerto Rico".
Performing arts
The Luis A. Ferré Performing Arts Center (Spanish: ''Centro de Bellas Artes Luis A. Ferré'') hosts some of the most important musical and artistic events in Puerto Rico. It is home to the Puerto Rico Symphony Orchestra (PRSO) and hosts the Casals Festival, the most important classical music festival in the Caribbean. The venue also hosts theater and musical performances such as Hamilton (musical), Hamilton, which it hosted in 2019. The Conservatory of Music of Puerto Rico is a public music conservatory that hosts Puerto Rican and international students has a longstanding relationship with the classical music movement in the island. The Ateneo Puertorriqueño and the theater of the University of Puerto Rico, Río Piedras Campus, University of Puerto Rico, Rio Piedras also host important music events.
Museums

The city is also the home of contemporary and classic art museums. The Museum of Art of Puerto Rico, Puerto Rico Museum of Art hosts the largest collection of contemporary art in Puerto Rico, housing over 1,100 permanent art pieces and displaying temporary exhibitions containing artwork from various locations through Latin America. The Puerto Rico Museum of Contemporary Art, located in Santurce, specializes in contemporary artwork from Latin America and the Caribbean. The paintings displayed in the permanent exhibition are either acquired by the museum's administrative personnel or donated by artists and collectors. They are judged by a panel of painters, art critics, and scholars before being displayed.
Other museums such as the Pablo Casals Museum, the San Juan Book Museum, the Museum of the Americas (San Juan, Puerto Rico), Museum of the Americas, and the Galería Nacional, National Gallery display historic items and artwork alongside contemporary art. Miscellaneous museums such as the Children's Museum, the Museo de Vida Silvestre, San Juan Wildlife Museum, and the Bacardi Distillery (also known as the "Rum Cathedral") in nearby Cataño appeal to different audiences through interactive exhibitions.
The Casa Dra. Concha Melendez Ramirez in Santurce is a National Historic Landmark and museum and research center that showcases the life and work of Concha Meléndez, one of the most important figures in the literary culture of Puerto Rico.
Old San Juan
Old San Juan ( es, Viejo San Juan) is a historic district located at the "northwest triangle" of the islet of San Juan. Its area roughly correlates to the Ballajá, Catedral, Marina, Mercado, San Cristóbal, and San Francisco sub-barrios (s ...
is also home to important art museums, such as the Galería Nacional, Puerto Rico National Gallery, and numerous private art galleries.
Government
Structure

As one of Puerto Rico's 78 Municipalities of Puerto Rico, municipalities, San Juan's government consists of two branches, the executive and the legislative. Those citizens eligible to vote directly elect the Mayor of San Juan and the municipal assembly for four-year terms. The municipal government is housed in San Juan City Hall, City Hall or ''Casa Alcaldia'', which is located at 153 San Francisco Street, facing the
Plaza de Armas
The ''Plaza de Armas'' (literally Weapons Square, but better translated as Parade Square or parade ground) is the name for Latin American main squares. In the central region of Mexico this space is known as El Zócalo and in Central America as ...
at the center of
Old San Juan
Old San Juan ( es, Viejo San Juan) is a historic district located at the "northwest triangle" of the islet of San Juan. Its area roughly correlates to the Ballajá, Catedral, Marina, Mercado, San Cristóbal, and San Francisco sub-barrios (s ...
.
City Hall was constructed based on Madrid, Spain, Madrid's City Hall starting in 1604 and finally completed in 1789.
The executive branch is headed by a popularly elected mayor. The office is held by Miguel Romero, Miguel Romero Lugo who won in the Puerto Rican general election, 2020, 2020 general election. Miguel Romero, Miguel Romero Lugo took over from Carmen Yulín Cruz, who was elected at the Puerto Rican general election, 2012, 2012 general election. Before her, Jorge A. Santini held the position for 12 years. In addition to running the city's day-to-day operations and supervising associated departments, the mayor is responsible for appointing a secretary-auditor and a treasurer. San Juan's Municipal Legislature is made up of 17 municipal legislators, elected at-large, which represent the city's population.
Coat of arms and flag

The has an official flag and coat of arms.
On March 8, 1948, the city government of San Juan officially adopted as the city's first flag an orange field, in the center of which is the coat of arms of the city. The orange color was based and taken from Father Diego de Torres Vargas' text and it reads:
"''Escudo de armas dado a Puerto Rico por los Reyes Católicos en el año de 1511, siendo Procurador un vecino llamado Pedro Moreno. Son : un cordero blanco con su banderilla colorada, sobre un libro, y todo sobre una isla verde, que es la de Puerto Rico, y por los lados una F y una I, que quiere decir Fernando e Isabel, los Reyes Católicos que se las dieron, y hoy se conservan en el estandarte real, que es de damasco anaranjado, con que se ganó la ciudad''".
("Coat of arms given to Puerto Rico by the Catholic Monarchs in the year 1511 being Procurator a ''vecino'' (citizen) named Pedro Moreno. They are a white lamb with a red flag, on top of a book, and everything above a green island, which is Puerto Rico...which is of orange damask, with which the city was won"). It appears that the color was changed from orange to white at some point.
Territorial and federal government

San Juan is the territorial capital of the Puerto Rico, Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, and it is home to the Executive branch of the government of Puerto Rico, executive, Legislative Assembly of Puerto Rico, legislative and Judiciary of Puerto Rico, judicial branches of the Government of Puerto Rico, Puerto Rican government. San Juan is also the seat of the Puerto Rico Senatorial district I, which is represented by two Senators. The United States District Court for the District of Puerto Rico is located in
Hato Rey
Hato Rey is a former barrio located in the northwest part of the dissolved municipality of Río Piedras. It now stretches over three barrios, of the municipality of San Juan, Puerto Rico:
Urban landscape
Its name means "king's cattle farm" (' ...
. There are two additional federal offices in the San Juan metropolitan area: the Jose V. Toledo Federal Building and United States Courthouse, Jose V. Toledo U.S. Post Office and Courthouse in Old San Juan and the GSA Federal Center in Guaynabo. The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), along with other federal organisms, has also had regional offices at the Federico Degetau Federal Building also in Hato Rey.
Safety
Law enforcement in San Juan is the joint responsibility of the Department of Police and Public Safety, also known as the San Juan Police Department and the Puerto Rico Police Department. The Municipal Police, originally known as the "San Juan Municipal Guard", was created in 1521 and had active military and law enforcement functions until 1980, when Act #77 created municipal law enforcement agencies in Puerto Rico. It employs over 1,000 sworn officers plus civilian staff.
Crime
In 2010 there were 201 homicides in San Juan, a rate of around 50 per 100,000 residents. In 2019 they were 172 homicides a rate of 53 per 100,000 residents. In the 2019 bulletin ranking of the 50 most violent cities in the world San Juan ranked as the 16th most violent in the world with a rate of 54.01 murders per 100,000 inhabitans,
and the 3rd most violent in the United States and its territories after St. Louis and Baltimore.
Media
Newspapers
Most of Puerto Rico's major newspapers are published in San Juan: El Nuevo Día, Primera Hora (Puerto Rico), Primera Hora, El Vocero and the English-language The San Juan Star, San Juan Star. Other newspapers published in San Juan are Metro Newspapers, Metro Puerto Rico, Indice and Caribbean Business, Caribbean Business News.
Radio
San Juan is also home to several of Puerto Rico's major radio stations: WKAQ (AM), WKAQ 580 AM and WKAQ-FM, 105 FM, WPRM Salsoul 99.1 FM, WODA La Nueva 94 FM, Fidelity 95.7 FM, WSKN Radio Isla 1320 AM, WORO Radio Oro 92.5 FM, Salsa Hits Radio, WAPA Radio, WOYE Magic 97.3, WRTU Radio Universidad FM, WIPR 940 AM, Mix 107.7 FM, WTOK Hot 102, AZ Rock, Radio Antillas, etc.
Television
Some of the television states based in San Juan are WKAQ-TV Telemundo/NBC, NBC Puerto Rico, Univision Puerto Rico, WORA Univision Puerto Rico, WAPA-TV, WIPR-TV, Mega TV (American TV network), WTCV Mega TV, WJPX América TeVé, etc.
Movies and filming
San Juan has been the setting of numerous movies and the city has also been used as a stand-in or substitute for other cities and countries where filming is more expensive, more dangerous or more restrictive. Some of the most popular movies filmed in San Juan are: Woody Allen's Bananas (film), Bananas (1971), Captain Ron (1992), Assassins (1995 film), Assassins (1995), Amistad (film), Amistad (1997), Bad Boys II (2003) standing-in as Havana, Dirty Dancing: Havana Nights (2004) also as Havana, The Men Who Stare at Goats (film), The Men Who Stare at Goats (2009) standing-in as Iraq, The Losers (2010 film), The Losers (2010), Fast Five (2011) stading-in as Miami and Rio de Janeiro, Pirates of the Caribbean: On Stranger Tides (2011) standing-in as Cádiz, Cádiz, Spain, The Rum Diary (film), The Rum Diary (2011), 22 Jump Street (2014) standing-in as a Mexican resort, Captain America: Civil War (2016) standing-in as Lagos, Lagos, Nigeria, Force of Nature (2020 film), Force of Nature (2020), and Black Panther: Wakanda Forever (2022).
Education
Colleges and universities

San Juan is home to many of Puerto Rico's institutions of higher learning. The UPRRP, University of Puerto Rico Río Piedras Campus is located in San Juan, along with the University of Puerto Rico, Medical Sciences Campus, University of Puerto Rico's Medical Sciences Campus. Other colleges located in San Juan are the University of the Sacred Heart (Puerto Rico), University of the Sacred Heart, the Polytechnic University of Puerto Rico, the Ana G. Méndez University System's Metropolitan University (Puerto Rico), Metropolitan University, the Metropolitan Campus of the Inter American University of Puerto Rico, the Carlos Albizu University, the Evangelic Seminary of Puerto Rico and the Center for Advanced Studies on Puerto Rico and the Caribbean. There are smaller colleges located in the city, including the ICPR Junior College, the ''Instituto de Banca y Comercio'' and the International Junior College, located in Santurce.
There are also several technical schools based in San Juan, including the Technological College of San Juan, the ''Liceo de Artes y Ciencias'', Ramirez College of Business and Technology, and the Puerto Rico Technical Junior College. The Puerto Rico Conservatory of Music and the Escuela de Artes Plásticas y Diseño de Puerto Rico, School of Fine Arts in Old San Juan specialize in education that promotes the fine arts and music.
Public and private schools
As of the 2022-23 school year, there are 83 public schools serving 24,494 students in San Juan, all of which are operated by the Puerto Rico Department of Education. Most of the specialized schools operated by the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico are located in San Juan. These schools emphasize topics such as Science and Math, Radio and Television, Arts, Trade, Music, and Sports, but also include other subjects such as Spanish, English, and Social Studies in their curriculum.
In addition to dozens of state-run elementary, intermediate, and high schools, the government of the city of San Juan operates two bilingual schools, including one sports-magnet school, the first municipal-run schools in Puerto Rico. Several private schools are located in San Juan, including Robinson and St. John's schools in the Condado (Santurce), Condado, Perpetuo Socorro in Miramar, Puerto Rico, Miramar, St. John's Episcopal, Santa Mónica and Academia San Jorge in
Santurce, Commonwealth High School, La Merced and Espíritu Santo in
Hato Rey
Hato Rey is a former barrio located in the northwest part of the dissolved municipality of Río Piedras. It now stretches over three barrios, of the municipality of San Juan, Puerto Rico:
Urban landscape
Its name means "king's cattle farm" (' ...
, Escuela Josefita Monserrate de Selles, San Antonio, Colegio San Ignacio de Loyola, San José in Río Piedras and Cupeyville School, Cupeyville, St. Mary's, Boneville and Cupey Maria Montesory School in Cupey.
Transportation
Airports

The San Juan–Caguas–Guaynabo metropolitan area, San Juan Metropolitan Area is served by two airports:
The Luis Muñoz Marín International Airport (SJU), San Juan's primary commercial airport, is located eight miles () from
Old San Juan
Old San Juan ( es, Viejo San Juan) is a historic district located at the "northwest triangle" of the islet of San Juan. Its area roughly correlates to the Ballajá, Catedral, Marina, Mercado, San Cristóbal, and San Francisco sub-barrios (s ...
in the neighboring municipality of
Carolina. The airport accommodates more than 30 domestic and international airlines and is the busiest airport in the Caribbean. It is often referred to as ''The Gateway to the Caribbean'' because it serves as the main connection to the island and the rest of the Caribbean for the United States and vice versa.
The area's secondary airport is the Fernando Ribas Dominicci Airport (SIG), located directly across the San Antonio Channel (''Caño San Antonio'') from Old San Juan in the
Isla Grande
Isla Grande is a small island and Corregimientos of Panama, corregimiento in Portobelo District, Colón Province, Panama, off the Caribbean coast. It had a population of 1,037 . Its population as of 1990 was 626; its population as of 2000 was 1,05 ...
district. Dominicci Airport is used mainly by general aviation aircraft, charter flights and some domestic commercial flights. It used to be the city's and also the island of Puerto Rico's main international gateway until the opening of Luis Muñoz Marin International Airport. It is now also widely used by the Isla Grande Flight School and Caribbean Flight Center, the only flight school on the island.
Highways and roads

Some of the major highways and roads of San Juan include:
* Puerto Rico Highway 52 (PR-52), also known as Luis A. Ferré Highway, runs from
Santurce to Ponce, Puerto Rico, Ponce through
Caguas
Caguas (, ) is a city and municipality of Puerto Rico located in the Central Mountain Range of Puerto Rico, south of San Juan and Trujillo Alto, west of Gurabo and San Lorenzo, and east of Aguas Buenas, Cidra, and Cayey. Caguas was founde ...
.
* Puerto Rico Highway 1 (PR-1), also known as Carretera Central (Puerto Rico), Carretera Central, Antigua Carretera Militar and ''La Muda'' between Río Piedras, Puerto Rico, Río Piedras and Caguas, runs from Santurce to Ponce through Cayey, Puerto Rico, Cayey and the
Cordillera Central.
* Puerto Rico Highway 2 (PR-2), also known as Kennedy Expressway between San Juan and
Guaynabo
Guaynabo (, ) is a city, suburb of San Juan and municipality in the northern part of Puerto Rico, located in the northern coast of the island, north of Aguas Buenas, south of Cataño, east of Bayamón, and west of San Juan. Guaynabo is spr ...
, runs from Santurce to Ponce through Mayagüez, Puerto Rico, Mayagüez.
* Puerto Rico Highway 3 (PR-3), also known as 65 de Infantería Avenue between Río Piedras and Carolina, runs from
Hato Rey
Hato Rey is a former barrio located in the northwest part of the dissolved municipality of Río Piedras. It now stretches over three barrios, of the municipality of San Juan, Puerto Rico:
Urban landscape
Its name means "king's cattle farm" (' ...
to Salinas, Puerto Rico, Salinas through Humacao, Puerto Rico, Humacao.
* Puerto Rico Highway 22 (PR-22), also known as José de Diego Expressway, runs from Santurce to Hatillo, Puerto Rico, Hatillo.
* Puerto Rico Highway 8 (PR-8) runs from Sabana Llana Norte to barrio Oriente and the Luis Muñoz Marín International Airport.
* Puerto Rico Highway 16 (PR-16) runs parallel to PR-1 from the Port of San Juan in Hato Rey to the Fernando Luis Ribas Dominicci Airport in
Isla Grande
Isla Grande is a small island and Corregimientos of Panama, corregimiento in Portobelo District, Colón Province, Panama, off the Caribbean coast. It had a population of 1,037 . Its population as of 1990 was 626; its population as of 2000 was 1,05 ...
.
* Puerto Rico Highway 18 (PR-18), also known as Las Américas Expressway, runs from Hato Rey Norte to Monacillo Urbano, San Juan, Puerto Rico, Monacillo Urbano.
* Puerto Rico Highway 20 (PR-20), also known as Rafael Martínez Nadal Expressway, runs from Guaynabo barrio-pueblo, Guaynabo Pueblo through Monacillo Urbano and
Gobernador Piñero to Pueblo Viejo, Guaynabo, Puerto Rico, Caparra.
* Puerto Rico Highway 26 (PR-26), also known as Román Baldorioty de Castro Expressway, runs from Santurce to the Luis Muñoz Marín International Airport and
Carolina.
* Puerto Rico Highway 28 (PR-28), also known as Francisco José de Goya Avenue, runs from the Port of San Juan to
Bayamón.
There are 193 bridges in San Juan.
Public transport

At 4,300 vehicles per paved mile, San Juan has by far the highest density of vehicles on the road of any city in the world. The city is served by five limited-access expressways and highways and numerous arterial avenues and boulevards but continues to suffer from severe traffic congestion.
The Puerto Rico Metropolitan Bus Authority, Metropolitan Bus Authority (''Autoridad Metropolitana de Autobuses'' or ''AMA'' in Spanish) provides daily bus transportation to residents of San Juan, Guaynabo, Bayamón, Toa Baja, Trujillo Alto, Cataño and Carolina through 30 fixed routes. Its fleet consists of 277 regular buses and 35 handicap-accessible buses. AMA's ridership is estimated at 112,000 on weekdays.
In an attempt to decrease vehicle dependency and road congestion, the city built a rapid transit, metro system dubbed "Tren Urbano" ("Urban Train"). The line connects to 16 stations. The project, which opened in late 2004, cost $2.25 billion and was more than $1 billion over budget and four years late. The Tren Urbano has received less ridership than was originally projected and has not significantly reduced the city's automobile traffic, despite a reported 7.5% ridership increase in 2006 over 2005. There is a planned project to build an "interurban light rail system" connecting the cities of San Juan-Caguas Rail, San Juan and Caguas.
Increased investment in public transportation, however, has not changed the fact that San Juan is an Automobile dependency, automobile-reliant city and its fast growth has sparked urban sprawl. As of mid-2010, the government has approved plans for a redesign of this Puerto Rican city, featuring a new mass transit system, new roads and intersections, and more beach-access points. Road space rationing, No cars will be allowed inside the oldest part of city (Old San Juan). The plans hope to remedy previous poor urban planning in the oldest section of the city, the Isleta, while curbing reliance on motor vehicles. The plans for redevelopment also hope to make the city more appealing in order to attract new residents, as San Juan has suffered from a shrinking population over the past 60 years.
Port

The Port of San Juan is the fourth busiest seaport in the Western Hemisphere, ranked among the top 17 in the world in terms of container movement. It is also the largest home-based cruise port in the world with over a dozen cruise ships. It is the second busiest port in cruise volume after Miami. It is managed by the Puerto Rico Ports Authority.
AcuaExpreso is a ferry service in the
San Juan Bay
San Juan Bay ( es, Bahía de San Juan) is the bay and main inlet adjacent to Old San Juan in northeastern Puerto Rico. It is about in length, the largest body of water in an estuary of about of channels, inlets and eight interconnected lagoons ...
, consisting of the Cataño Ferry (''Lancha de Cataño'') service between Cataño barrio-pueblo, downtown Cataño and
Old San Juan
Old San Juan ( es, Viejo San Juan) is a historic district located at the "northwest triangle" of the islet of San Juan. Its area roughly correlates to the Ballajá, Catedral, Marina, Mercado, San Cristóbal, and San Francisco sub-barrios (s ...
, and the ''AquaExpress'' which connects Old San Juan to
Hato Rey
Hato Rey is a former barrio located in the northwest part of the dissolved municipality of Río Piedras. It now stretches over three barrios, of the municipality of San Juan, Puerto Rico:
Urban landscape
Its name means "king's cattle farm" (' ...
and the Hato Rey station, Tren Urbano.
Healthcare

San Juan has an elaborate system of triage, hospital, and preventive care health services. The municipal government sponsors regular health fairs in different areas of the city focusing on health care for the elderly and the disabled. There are 20 hospitals in San Juan, half of them operated by the government. The largest hospital in San Juan and most important of Puerto Rico and the Caribbean is the Rio Piedras Medical Center, or ''Centro Medico de Rio Piedras'' in Spanish. This hospital, founded in 1956, is operated by the Medical Services Administration of the Department of Health of Puerto Rico. It is made up of eight other hospitals.
* San Juan Municipal Hospital: This hospital is operated by the San Juan municipal government.
* Industrial Hospital: This is the hospital for Puerto Rico government employees, whether municipal or Commonwealth government employees. Normally, injured police officers and firefighters are cared for here.
* San Juan Pediatric Hospital - Also operated by the San Juan municipal government.
* Pediatric Hospital: Operated by the government of the Commonwealth, this is the main trauma hospital for pediatric cases.
* Centro Médico: This is the main hospital for trauma cases for Puerto Rico and the Caribbean.
* Centro Cardiovascular del Caribe (Caribbean Cardiovascular Center): This is the main hospital for open heart surgery in the Caribbean. It features a hotel for the patients' families.
* Psychiatric Hospital: The main psychiatric hospital in Puerto Rico. Operated by the government of Puerto Rico.
* Psychiatric Correctional Hospital: It is both a hospital and correctional facility. It is operated jointly by the Puerto Rico Department of Corrections and the Medical Services Administration.
The city of San Juan operates 10 hospitals. Of these, nine are Diagnostic and Treatment Centers located in communities throughout San Juan. The main hospital is located at Centro Medico. These 10 hospitals are:
*
La Perla
* Puerta de Tierra, Puerto Rico, Puerta de Tierra
* Llorens Torres
* Puerto Nuevo
* San José
* Rio Piedras
* Sabana Llana
* Hoare
* Santurce Parada 19
* General Hospital (Centro Medico)
Also, there are 10 private hospitals in San Juan. These are:
* Hospital Metropolitano
* Hospital Auxilio Mutuo
* Hospital Auxilio Mutuo Expreso
* Hospital de Veteranos: The main Veterans hospital in the Caribbean. Operated by the U.S. Veteran Healthcare System.
* Ashford Presbyterian Hospital
* Hospital Pavia Hato Rey
* Hospital Pavia Santurce
* San Jorge Children's Hospital: The most well-known children's hospital in the San Juan Metropolitan Area.
* Hospital San Gerardo: Located at the Cupey neighborhood, is a small hospital but is also specialized in psychiatry and elderly.
* Hospital del Maestro (Teachers Hospital): Located in Hato Rey, this hospital is operated by the Puerto Rico Teachers Association.
Sports

Teams based in San Juan have been notably successful in athletic competition. The Santurce Crabbers (basketball), Santurce Crabbers won the National Superior Basketball League championship in 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001 and 2003 during this period being recognized as a dynasty. The San Juan Senators and the Santurce Crabbers (baseball), Santurce Crabbers were the two major baseball teams in the city, winning the championship of the Puerto Rican Professional Baseball League a total of 17 times. The Santurce Crabbers are located third among teams with more championships in the
Caribbean Series
The Caribbean Series (''Spanish'': ''Serie del Caribe''), also called Caribbean World Series, is the highest tournament for professional baseball teams in Latin America. The tournament location is rotated annually among the countries and is norma ...
, winning championships in the 1951, 1953, 1955, 1993 and 2000 editions of the tournament. The city has also been the host of events within the sports community; some examples include:
* Host of the 1966 Central American and Caribbean Games.
* Host of the 1979 Pan American Games.
* Hosted the Caribbean World Series nine times.
* Major League Baseball's Montreal Expos played 22 home games at
Hiram Bithorn Stadium
Hiram Bithorn Stadium (Spanish: Estadio Hiram Bithorn) is a baseball park in San Juan, Puerto Rico, built in 1962 and designed by Puerto Rican architect Pedro Miranda. It is operated by the municipal government of the city of San Juan. Its name ho ...
between 2003 and 2004. The team also briefly considered moving permanently to San Juan before relocating to Washington, D.C.
* Hosted the 2006 World Baseball Classic, 2006, 2009 World Baseball Classic, 2009 and 2013 World Baseball Classic at the
Hiram Bithorn Stadium
Hiram Bithorn Stadium (Spanish: Estadio Hiram Bithorn) is a baseball park in San Juan, Puerto Rico, built in 1962 and designed by Puerto Rican architect Pedro Miranda. It is operated by the municipal government of the city of San Juan. Its name ho ...
.
* Host of the 1974 FIBA World Championship (basketball).
* Host of the FIBA Americas Championship five times (1980, 1993, 1999, 2003, 2009).
* Hosted the very first edition of World Wrestling Entertainment's pay per view New Year's Revolution was held at the José Miguel Agrelot Coliseum in January 2005.
* The Latin American Regional
Special Olympics
Special Olympics is the world's largest sports organization for children and adults with intellectual disabilities and physical disabilities, providing year-round training and activities to 5 million participants and Unified Sports partners in ...
in February 2010.
* Host of Major League Baseball's 2010 "San Juan Series", three games of the Mets at Marlins held on June 28–30, 2010 at
Hiram Bithorn Stadium
Hiram Bithorn Stadium (Spanish: Estadio Hiram Bithorn) is a baseball park in San Juan, Puerto Rico, built in 1962 and designed by Puerto Rican architect Pedro Miranda. It is operated by the municipal government of the city of San Juan. Its name ho ...
.
The $28 million San Juan Natatorium attracts island-wide and regional swim meets, as well as winter training by top-rated mainland U.S. colleges and universities, including the United States Military Academy at West Point and the United States Naval Academy at Annapolis.
In July 2007, the San Juan Golf Academy and its driving range began operating atop the city's former sanitary landfill in
Puerto Nuevo, and will eventually include the city's first and only 9-hole golf course.
Professional teams
International relations
Diplomatic missions
Twin towns – Sister cities
San Juan is Twin towns and sister cities, twinned with:
Notable people from San Juan
See also
* History of Puerto Rico
* List of former national capitals
* List of national capitals
* List of people from San Juan, Puerto Rico
* List of streets in San Juan, Puerto Rico
* Military history of Puerto Rico
* National Register of Historic Places listings in San Juan, Puerto Rico
* Spanish Colonial style
Notes
References
Bibliography
External links
City of San JuanNational Park Service – San JuanHistoric Places in Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands, a National Park Service Discover Our Shared Heritage Travel ItineraryNational Weather Service – San Juan, Puerto RicoSan Juan Puerto Rico
{{DEFAULTSORT:San Juan, Puerto Rico
San Juan, Puerto Rico,
Municipalities of Puerto Rico
Bermuda Triangle
Capitals in North America
Capitals in the Caribbean
Capitals of political divisions in the United States
Populated coastal places in Puerto Rico
Populated places established in 1508
Port cities in Puerto Rico
San Juan–Caguas–Guaynabo metropolitan area
1508 establishments in the Spanish Empire
1508 establishments in North America
 San Juan, as a settlement of the
San Juan, as a settlement of the  On May 8, 1898, United States Navy ships, among them , , , , and , commanded by Rear Admiral
On May 8, 1898, United States Navy ships, among them , , , , and , commanded by Rear Admiral 
 San Juan is located along the north-eastern coast of Puerto Rico in the Northern Plains region. It lies south of the Atlantic Ocean; north of
San Juan is located along the north-eastern coast of Puerto Rico in the Northern Plains region. It lies south of the Atlantic Ocean; north of  As with other parts of Puerto Rico and the Caribbean, San Juan is often blanketed by waves of
As with other parts of Puerto Rico and the Caribbean, San Juan is often blanketed by waves of 
 San Juan is home to numerous
San Juan is home to numerous  The San Juan Ecological Corridor is a conservation project by the
The San Juan Ecological Corridor is a conservation project by the 
 Some of the recreational parks of the municipality include Bahía Urbana, a waterfront park located in Old San Juan and Puerta de Tierra by the San Juan Bay; the Paseo de Puerta de Tierra, a recreational walkway along the Atlantic Ocean cliffs of Puerta de Tierra that connects the Puerto Rico Capitol with
Some of the recreational parks of the municipality include Bahía Urbana, a waterfront park located in Old San Juan and Puerta de Tierra by the San Juan Bay; the Paseo de Puerta de Tierra, a recreational walkway along the Atlantic Ocean cliffs of Puerta de Tierra that connects the Puerto Rico Capitol with 

 As with the other Puerto Rican municipalities, San Juan is administratively divided into ''Barrios of Puerto Rico, barrios.'' What is now known as
As with the other Puerto Rican municipalities, San Juan is administratively divided into ''Barrios of Puerto Rico, barrios.'' What is now known as 
 During the Spanish colonial times most of the urban population resided in what is today known as
During the Spanish colonial times most of the urban population resided in what is today known as  Santurce is the largest and most populated barrio in the municipality of San Juan, and one of the most densely populated areas of the island (13,257.4 persons per square mile). Santurce, originally named ''San Mateo de Cangrejos'' (Saint Matthew of the Crabs), was a settlement for Freedman, freed African slaves during the early days of the city. After Pablo Ubarri Capetillo, a Spanish railroad developer and ''Count of San José de Santurce'' under the Spanish colonial period, sought permission to link San Juan with Río Piedras proper via steam tramway in 1878, the time it took to travel between both points were shortened and thereby stimulated the colonization and growth of the district. At the beginning of the twentieth century an electric trolley was installed, the township was split into three parts, and its main settlement, merged with the city, was renamed using the Spanish spelling of Santurtzi (''Saint George'' in Basque), Ubarri's birthplace in Biscay, Vizcaya, Spain. The "Museo de Arte de Puerto Rico" (Puerto Rico Museum of Art) and other important cultural venues are located in Santurce.
This barrio is further divided into subbarrios such as the tourist-oriented neighborhood of Condado (Santurce), Condado, which occupies land that used to be owned by Ubarri Capetillo. Beaches such as nearby Ocean Park, popular with swimmers, surfers and kitesurfers, are found all along the district's Atlantic coastline which is also the locus of numerous hotels. Miramar (Santurce), Miramar is mainly a residential area rising south of the Condado Lagoon. It comprises the former ''barrio'' of Miraflores, as well as drained marshland and landfill over which was built San Juan's first airport, the Isla Grande airport, which was renamed Fernando Luis Ribas Dominicci Airport in honor of Major Fernando Luis Ribas-Dominicci (USAF). Miramar now hosts the
Santurce is the largest and most populated barrio in the municipality of San Juan, and one of the most densely populated areas of the island (13,257.4 persons per square mile). Santurce, originally named ''San Mateo de Cangrejos'' (Saint Matthew of the Crabs), was a settlement for Freedman, freed African slaves during the early days of the city. After Pablo Ubarri Capetillo, a Spanish railroad developer and ''Count of San José de Santurce'' under the Spanish colonial period, sought permission to link San Juan with Río Piedras proper via steam tramway in 1878, the time it took to travel between both points were shortened and thereby stimulated the colonization and growth of the district. At the beginning of the twentieth century an electric trolley was installed, the township was split into three parts, and its main settlement, merged with the city, was renamed using the Spanish spelling of Santurtzi (''Saint George'' in Basque), Ubarri's birthplace in Biscay, Vizcaya, Spain. The "Museo de Arte de Puerto Rico" (Puerto Rico Museum of Art) and other important cultural venues are located in Santurce.
This barrio is further divided into subbarrios such as the tourist-oriented neighborhood of Condado (Santurce), Condado, which occupies land that used to be owned by Ubarri Capetillo. Beaches such as nearby Ocean Park, popular with swimmers, surfers and kitesurfers, are found all along the district's Atlantic coastline which is also the locus of numerous hotels. Miramar (Santurce), Miramar is mainly a residential area rising south of the Condado Lagoon. It comprises the former ''barrio'' of Miraflores, as well as drained marshland and landfill over which was built San Juan's first airport, the Isla Grande airport, which was renamed Fernando Luis Ribas Dominicci Airport in honor of Major Fernando Luis Ribas-Dominicci (USAF). Miramar now hosts the  South of Santurce is
South of Santurce is  San Juan experienced significant economic growth following World War II. During this period the city underwent an industrial revolution, although as of 1984 it had never generated its own economic region.Microsoft Encarta Biblioteca (2006), Microsoft Corporation The city's economy relies mostly on companies dedicated to the manufacture of several products, including: chemical substances (bleach and house cleaning products); pharmaceuticals; rum and other beverages; fertilizers; electric tools; Electronics, electronic devices; plastics, textiles, and food-based products.
Tourism is also a key industry, based on San Juan's proximity to Puerto Rico's main airport, the Luis Muñoz Marín International Airport.
The tourism focus of the city is located in the district of Condado Beach where there are luxurious hotels. Historical locations such as El Morro, Old San Juan and El Cuartel de Ballaja are promoted in tourism campaigns. The district of Hato Rey contains a corporate sector known as Milla de Oro (Golden Mile) which serves as the headquarters of local and international banks. San Juan's Hato Rey district is often referred to as the "Wall Street of the Caribbean", due to the influence of the area on Puerto Rico and the Caribbean's economy.
San Juan is also home to the Popular, Inc., parent company of Banco Popular de Puerto Rico, Popular Bank, E-Loan, and a Fortune 1000 company as of 2022. Other companies based in San Juan include ATH (interbank network), ATH Network, First BanCorp, Liberty Puerto Rico, The Cervantes Group, and Triple-S Management Corporation. Seaborne Airlines is headquartered on the ninth floor of the World Plaza Building in Hato Rey.
San Juan experienced significant economic growth following World War II. During this period the city underwent an industrial revolution, although as of 1984 it had never generated its own economic region.Microsoft Encarta Biblioteca (2006), Microsoft Corporation The city's economy relies mostly on companies dedicated to the manufacture of several products, including: chemical substances (bleach and house cleaning products); pharmaceuticals; rum and other beverages; fertilizers; electric tools; Electronics, electronic devices; plastics, textiles, and food-based products.
Tourism is also a key industry, based on San Juan's proximity to Puerto Rico's main airport, the Luis Muñoz Marín International Airport.
The tourism focus of the city is located in the district of Condado Beach where there are luxurious hotels. Historical locations such as El Morro, Old San Juan and El Cuartel de Ballaja are promoted in tourism campaigns. The district of Hato Rey contains a corporate sector known as Milla de Oro (Golden Mile) which serves as the headquarters of local and international banks. San Juan's Hato Rey district is often referred to as the "Wall Street of the Caribbean", due to the influence of the area on Puerto Rico and the Caribbean's economy.
San Juan is also home to the Popular, Inc., parent company of Banco Popular de Puerto Rico, Popular Bank, E-Loan, and a Fortune 1000 company as of 2022. Other companies based in San Juan include ATH (interbank network), ATH Network, First BanCorp, Liberty Puerto Rico, The Cervantes Group, and Triple-S Management Corporation. Seaborne Airlines is headquartered on the ninth floor of the World Plaza Building in Hato Rey.

 Technological advances after World War II in the development of the airliner, coupled with the island's climate and natural setting, have transformed San Juan into the springboard for tourism around the island, and has made the rest of the Caribbean known throughout the world during the last fifty years. Today the capital features hotels, museums, historical buildings, restaurants, parks, beaches and shopping centers.
Old San Juan is often emphasized in tourism campaigns, promoting the historic nature of its colonial buildings and narrow streets covered by cobblestones, a blue stone cast from furnace slag; they were brought over as ballast on Spanish ships. This includes the city's ancient defensive wall and forts, most notably El Morro and the Castillo San Cristóbal (San Juan), Castillo San Cristóbal. On January 23, 1984, both of these edifices together with
Technological advances after World War II in the development of the airliner, coupled with the island's climate and natural setting, have transformed San Juan into the springboard for tourism around the island, and has made the rest of the Caribbean known throughout the world during the last fifty years. Today the capital features hotels, museums, historical buildings, restaurants, parks, beaches and shopping centers.
Old San Juan is often emphasized in tourism campaigns, promoting the historic nature of its colonial buildings and narrow streets covered by cobblestones, a blue stone cast from furnace slag; they were brought over as ballast on Spanish ships. This includes the city's ancient defensive wall and forts, most notably El Morro and the Castillo San Cristóbal (San Juan), Castillo San Cristóbal. On January 23, 1984, both of these edifices together with  Outside of Old San Juan, the Puerto Rico Convention Center District (PRCC) includes the
Outside of Old San Juan, the Puerto Rico Convention Center District (PRCC) includes the  San Juan is the birthplace of artists and musicians who have significantly influenced Puerto Rican culture. During the 20th century, the musical aspect of the city was influenced by performers including West Indian Americans, Afro-Caribbean dancer and choreographer Sylvia del Villard and José Enrique Pedreira who became a composer of Puerto Rican Music of Puerto Rico#Danza, ''Danzas''. International musicians such as opera singer Justino Díaz and Grammy Award winners Daddy Yankee, Ramón Ayala (Daddy Yankee) and Ricky Martin were born in the city. Other notable residents include writers Giannina Braschi and Tomás Blanco (writer), Tomas Blanco, award-winning actors Raul Julia and Benicio del Toro, and comedian José Miguel Agrelot. Rafael Cordero (educator), Rafael Cordero (1790–1868), was influential in the development of Puerto Rican education and has been once renowned as "The Father of Public Education in Puerto Rico".
San Juan is the birthplace of artists and musicians who have significantly influenced Puerto Rican culture. During the 20th century, the musical aspect of the city was influenced by performers including West Indian Americans, Afro-Caribbean dancer and choreographer Sylvia del Villard and José Enrique Pedreira who became a composer of Puerto Rican Music of Puerto Rico#Danza, ''Danzas''. International musicians such as opera singer Justino Díaz and Grammy Award winners Daddy Yankee, Ramón Ayala (Daddy Yankee) and Ricky Martin were born in the city. Other notable residents include writers Giannina Braschi and Tomás Blanco (writer), Tomas Blanco, award-winning actors Raul Julia and Benicio del Toro, and comedian José Miguel Agrelot. Rafael Cordero (educator), Rafael Cordero (1790–1868), was influential in the development of Puerto Rican education and has been once renowned as "The Father of Public Education in Puerto Rico".
 The city is also the home of contemporary and classic art museums. The Museum of Art of Puerto Rico, Puerto Rico Museum of Art hosts the largest collection of contemporary art in Puerto Rico, housing over 1,100 permanent art pieces and displaying temporary exhibitions containing artwork from various locations through Latin America. The Puerto Rico Museum of Contemporary Art, located in Santurce, specializes in contemporary artwork from Latin America and the Caribbean. The paintings displayed in the permanent exhibition are either acquired by the museum's administrative personnel or donated by artists and collectors. They are judged by a panel of painters, art critics, and scholars before being displayed.
Other museums such as the Pablo Casals Museum, the San Juan Book Museum, the Museum of the Americas (San Juan, Puerto Rico), Museum of the Americas, and the Galería Nacional, National Gallery display historic items and artwork alongside contemporary art. Miscellaneous museums such as the Children's Museum, the Museo de Vida Silvestre, San Juan Wildlife Museum, and the Bacardi Distillery (also known as the "Rum Cathedral") in nearby Cataño appeal to different audiences through interactive exhibitions.
The Casa Dra. Concha Melendez Ramirez in Santurce is a National Historic Landmark and museum and research center that showcases the life and work of Concha Meléndez, one of the most important figures in the literary culture of Puerto Rico.
The city is also the home of contemporary and classic art museums. The Museum of Art of Puerto Rico, Puerto Rico Museum of Art hosts the largest collection of contemporary art in Puerto Rico, housing over 1,100 permanent art pieces and displaying temporary exhibitions containing artwork from various locations through Latin America. The Puerto Rico Museum of Contemporary Art, located in Santurce, specializes in contemporary artwork from Latin America and the Caribbean. The paintings displayed in the permanent exhibition are either acquired by the museum's administrative personnel or donated by artists and collectors. They are judged by a panel of painters, art critics, and scholars before being displayed.
Other museums such as the Pablo Casals Museum, the San Juan Book Museum, the Museum of the Americas (San Juan, Puerto Rico), Museum of the Americas, and the Galería Nacional, National Gallery display historic items and artwork alongside contemporary art. Miscellaneous museums such as the Children's Museum, the Museo de Vida Silvestre, San Juan Wildlife Museum, and the Bacardi Distillery (also known as the "Rum Cathedral") in nearby Cataño appeal to different audiences through interactive exhibitions.
The Casa Dra. Concha Melendez Ramirez in Santurce is a National Historic Landmark and museum and research center that showcases the life and work of Concha Meléndez, one of the most important figures in the literary culture of Puerto Rico.  San Juan is the territorial capital of the Puerto Rico, Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, and it is home to the Executive branch of the government of Puerto Rico, executive, Legislative Assembly of Puerto Rico, legislative and Judiciary of Puerto Rico, judicial branches of the Government of Puerto Rico, Puerto Rican government. San Juan is also the seat of the Puerto Rico Senatorial district I, which is represented by two Senators. The United States District Court for the District of Puerto Rico is located in
San Juan is the territorial capital of the Puerto Rico, Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, and it is home to the Executive branch of the government of Puerto Rico, executive, Legislative Assembly of Puerto Rico, legislative and Judiciary of Puerto Rico, judicial branches of the Government of Puerto Rico, Puerto Rican government. San Juan is also the seat of the Puerto Rico Senatorial district I, which is represented by two Senators. The United States District Court for the District of Puerto Rico is located in  San Juan is home to many of Puerto Rico's institutions of higher learning. The UPRRP, University of Puerto Rico Río Piedras Campus is located in San Juan, along with the University of Puerto Rico, Medical Sciences Campus, University of Puerto Rico's Medical Sciences Campus. Other colleges located in San Juan are the University of the Sacred Heart (Puerto Rico), University of the Sacred Heart, the Polytechnic University of Puerto Rico, the Ana G. Méndez University System's Metropolitan University (Puerto Rico), Metropolitan University, the Metropolitan Campus of the Inter American University of Puerto Rico, the Carlos Albizu University, the Evangelic Seminary of Puerto Rico and the Center for Advanced Studies on Puerto Rico and the Caribbean. There are smaller colleges located in the city, including the ICPR Junior College, the ''Instituto de Banca y Comercio'' and the International Junior College, located in Santurce.
There are also several technical schools based in San Juan, including the Technological College of San Juan, the ''Liceo de Artes y Ciencias'', Ramirez College of Business and Technology, and the Puerto Rico Technical Junior College. The Puerto Rico Conservatory of Music and the Escuela de Artes Plásticas y Diseño de Puerto Rico, School of Fine Arts in Old San Juan specialize in education that promotes the fine arts and music.
San Juan is home to many of Puerto Rico's institutions of higher learning. The UPRRP, University of Puerto Rico Río Piedras Campus is located in San Juan, along with the University of Puerto Rico, Medical Sciences Campus, University of Puerto Rico's Medical Sciences Campus. Other colleges located in San Juan are the University of the Sacred Heart (Puerto Rico), University of the Sacred Heart, the Polytechnic University of Puerto Rico, the Ana G. Méndez University System's Metropolitan University (Puerto Rico), Metropolitan University, the Metropolitan Campus of the Inter American University of Puerto Rico, the Carlos Albizu University, the Evangelic Seminary of Puerto Rico and the Center for Advanced Studies on Puerto Rico and the Caribbean. There are smaller colleges located in the city, including the ICPR Junior College, the ''Instituto de Banca y Comercio'' and the International Junior College, located in Santurce.
There are also several technical schools based in San Juan, including the Technological College of San Juan, the ''Liceo de Artes y Ciencias'', Ramirez College of Business and Technology, and the Puerto Rico Technical Junior College. The Puerto Rico Conservatory of Music and the Escuela de Artes Plásticas y Diseño de Puerto Rico, School of Fine Arts in Old San Juan specialize in education that promotes the fine arts and music.
 The San Juan–Caguas–Guaynabo metropolitan area, San Juan Metropolitan Area is served by two airports:
The Luis Muñoz Marín International Airport (SJU), San Juan's primary commercial airport, is located eight miles () from
The San Juan–Caguas–Guaynabo metropolitan area, San Juan Metropolitan Area is served by two airports:
The Luis Muñoz Marín International Airport (SJU), San Juan's primary commercial airport, is located eight miles () from  Some of the major highways and roads of San Juan include:
* Puerto Rico Highway 52 (PR-52), also known as Luis A. Ferré Highway, runs from Santurce to Ponce, Puerto Rico, Ponce through
Some of the major highways and roads of San Juan include:
* Puerto Rico Highway 52 (PR-52), also known as Luis A. Ferré Highway, runs from Santurce to Ponce, Puerto Rico, Ponce through  At 4,300 vehicles per paved mile, San Juan has by far the highest density of vehicles on the road of any city in the world. The city is served by five limited-access expressways and highways and numerous arterial avenues and boulevards but continues to suffer from severe traffic congestion.
The Puerto Rico Metropolitan Bus Authority, Metropolitan Bus Authority (''Autoridad Metropolitana de Autobuses'' or ''AMA'' in Spanish) provides daily bus transportation to residents of San Juan, Guaynabo, Bayamón, Toa Baja, Trujillo Alto, Cataño and Carolina through 30 fixed routes. Its fleet consists of 277 regular buses and 35 handicap-accessible buses. AMA's ridership is estimated at 112,000 on weekdays.
At 4,300 vehicles per paved mile, San Juan has by far the highest density of vehicles on the road of any city in the world. The city is served by five limited-access expressways and highways and numerous arterial avenues and boulevards but continues to suffer from severe traffic congestion.
The Puerto Rico Metropolitan Bus Authority, Metropolitan Bus Authority (''Autoridad Metropolitana de Autobuses'' or ''AMA'' in Spanish) provides daily bus transportation to residents of San Juan, Guaynabo, Bayamón, Toa Baja, Trujillo Alto, Cataño and Carolina through 30 fixed routes. Its fleet consists of 277 regular buses and 35 handicap-accessible buses. AMA's ridership is estimated at 112,000 on weekdays.
 In an attempt to decrease vehicle dependency and road congestion, the city built a rapid transit, metro system dubbed "Tren Urbano" ("Urban Train"). The line connects to 16 stations. The project, which opened in late 2004, cost $2.25 billion and was more than $1 billion over budget and four years late. The Tren Urbano has received less ridership than was originally projected and has not significantly reduced the city's automobile traffic, despite a reported 7.5% ridership increase in 2006 over 2005. There is a planned project to build an "interurban light rail system" connecting the cities of San Juan-Caguas Rail, San Juan and Caguas.
Increased investment in public transportation, however, has not changed the fact that San Juan is an Automobile dependency, automobile-reliant city and its fast growth has sparked urban sprawl. As of mid-2010, the government has approved plans for a redesign of this Puerto Rican city, featuring a new mass transit system, new roads and intersections, and more beach-access points. Road space rationing, No cars will be allowed inside the oldest part of city (Old San Juan). The plans hope to remedy previous poor urban planning in the oldest section of the city, the Isleta, while curbing reliance on motor vehicles. The plans for redevelopment also hope to make the city more appealing in order to attract new residents, as San Juan has suffered from a shrinking population over the past 60 years.
In an attempt to decrease vehicle dependency and road congestion, the city built a rapid transit, metro system dubbed "Tren Urbano" ("Urban Train"). The line connects to 16 stations. The project, which opened in late 2004, cost $2.25 billion and was more than $1 billion over budget and four years late. The Tren Urbano has received less ridership than was originally projected and has not significantly reduced the city's automobile traffic, despite a reported 7.5% ridership increase in 2006 over 2005. There is a planned project to build an "interurban light rail system" connecting the cities of San Juan-Caguas Rail, San Juan and Caguas.
Increased investment in public transportation, however, has not changed the fact that San Juan is an Automobile dependency, automobile-reliant city and its fast growth has sparked urban sprawl. As of mid-2010, the government has approved plans for a redesign of this Puerto Rican city, featuring a new mass transit system, new roads and intersections, and more beach-access points. Road space rationing, No cars will be allowed inside the oldest part of city (Old San Juan). The plans hope to remedy previous poor urban planning in the oldest section of the city, the Isleta, while curbing reliance on motor vehicles. The plans for redevelopment also hope to make the city more appealing in order to attract new residents, as San Juan has suffered from a shrinking population over the past 60 years.
 The Port of San Juan is the fourth busiest seaport in the Western Hemisphere, ranked among the top 17 in the world in terms of container movement. It is also the largest home-based cruise port in the world with over a dozen cruise ships. It is the second busiest port in cruise volume after Miami. It is managed by the Puerto Rico Ports Authority.
AcuaExpreso is a ferry service in the
The Port of San Juan is the fourth busiest seaport in the Western Hemisphere, ranked among the top 17 in the world in terms of container movement. It is also the largest home-based cruise port in the world with over a dozen cruise ships. It is the second busiest port in cruise volume after Miami. It is managed by the Puerto Rico Ports Authority.
AcuaExpreso is a ferry service in the  San Juan has an elaborate system of triage, hospital, and preventive care health services. The municipal government sponsors regular health fairs in different areas of the city focusing on health care for the elderly and the disabled. There are 20 hospitals in San Juan, half of them operated by the government. The largest hospital in San Juan and most important of Puerto Rico and the Caribbean is the Rio Piedras Medical Center, or ''Centro Medico de Rio Piedras'' in Spanish. This hospital, founded in 1956, is operated by the Medical Services Administration of the Department of Health of Puerto Rico. It is made up of eight other hospitals.
* San Juan Municipal Hospital: This hospital is operated by the San Juan municipal government.
* Industrial Hospital: This is the hospital for Puerto Rico government employees, whether municipal or Commonwealth government employees. Normally, injured police officers and firefighters are cared for here.
* San Juan Pediatric Hospital - Also operated by the San Juan municipal government.
* Pediatric Hospital: Operated by the government of the Commonwealth, this is the main trauma hospital for pediatric cases.
* Centro Médico: This is the main hospital for trauma cases for Puerto Rico and the Caribbean.
* Centro Cardiovascular del Caribe (Caribbean Cardiovascular Center): This is the main hospital for open heart surgery in the Caribbean. It features a hotel for the patients' families.
* Psychiatric Hospital: The main psychiatric hospital in Puerto Rico. Operated by the government of Puerto Rico.
* Psychiatric Correctional Hospital: It is both a hospital and correctional facility. It is operated jointly by the Puerto Rico Department of Corrections and the Medical Services Administration.
The city of San Juan operates 10 hospitals. Of these, nine are Diagnostic and Treatment Centers located in communities throughout San Juan. The main hospital is located at Centro Medico. These 10 hospitals are:
* La Perla
* Puerta de Tierra, Puerto Rico, Puerta de Tierra
* Llorens Torres
* Puerto Nuevo
* San José
* Rio Piedras
* Sabana Llana
* Hoare
* Santurce Parada 19
* General Hospital (Centro Medico)
Also, there are 10 private hospitals in San Juan. These are:
* Hospital Metropolitano
* Hospital Auxilio Mutuo
* Hospital Auxilio Mutuo Expreso
* Hospital de Veteranos: The main Veterans hospital in the Caribbean. Operated by the U.S. Veteran Healthcare System.
* Ashford Presbyterian Hospital
* Hospital Pavia Hato Rey
* Hospital Pavia Santurce
* San Jorge Children's Hospital: The most well-known children's hospital in the San Juan Metropolitan Area.
* Hospital San Gerardo: Located at the Cupey neighborhood, is a small hospital but is also specialized in psychiatry and elderly.
* Hospital del Maestro (Teachers Hospital): Located in Hato Rey, this hospital is operated by the Puerto Rico Teachers Association.
San Juan has an elaborate system of triage, hospital, and preventive care health services. The municipal government sponsors regular health fairs in different areas of the city focusing on health care for the elderly and the disabled. There are 20 hospitals in San Juan, half of them operated by the government. The largest hospital in San Juan and most important of Puerto Rico and the Caribbean is the Rio Piedras Medical Center, or ''Centro Medico de Rio Piedras'' in Spanish. This hospital, founded in 1956, is operated by the Medical Services Administration of the Department of Health of Puerto Rico. It is made up of eight other hospitals.
* San Juan Municipal Hospital: This hospital is operated by the San Juan municipal government.
* Industrial Hospital: This is the hospital for Puerto Rico government employees, whether municipal or Commonwealth government employees. Normally, injured police officers and firefighters are cared for here.
* San Juan Pediatric Hospital - Also operated by the San Juan municipal government.
* Pediatric Hospital: Operated by the government of the Commonwealth, this is the main trauma hospital for pediatric cases.
* Centro Médico: This is the main hospital for trauma cases for Puerto Rico and the Caribbean.
* Centro Cardiovascular del Caribe (Caribbean Cardiovascular Center): This is the main hospital for open heart surgery in the Caribbean. It features a hotel for the patients' families.
* Psychiatric Hospital: The main psychiatric hospital in Puerto Rico. Operated by the government of Puerto Rico.
* Psychiatric Correctional Hospital: It is both a hospital and correctional facility. It is operated jointly by the Puerto Rico Department of Corrections and the Medical Services Administration.
The city of San Juan operates 10 hospitals. Of these, nine are Diagnostic and Treatment Centers located in communities throughout San Juan. The main hospital is located at Centro Medico. These 10 hospitals are:
* La Perla
* Puerta de Tierra, Puerto Rico, Puerta de Tierra
* Llorens Torres
* Puerto Nuevo
* San José
* Rio Piedras
* Sabana Llana
* Hoare
* Santurce Parada 19
* General Hospital (Centro Medico)
Also, there are 10 private hospitals in San Juan. These are:
* Hospital Metropolitano
* Hospital Auxilio Mutuo
* Hospital Auxilio Mutuo Expreso
* Hospital de Veteranos: The main Veterans hospital in the Caribbean. Operated by the U.S. Veteran Healthcare System.
* Ashford Presbyterian Hospital
* Hospital Pavia Hato Rey
* Hospital Pavia Santurce
* San Jorge Children's Hospital: The most well-known children's hospital in the San Juan Metropolitan Area.
* Hospital San Gerardo: Located at the Cupey neighborhood, is a small hospital but is also specialized in psychiatry and elderly.
* Hospital del Maestro (Teachers Hospital): Located in Hato Rey, this hospital is operated by the Puerto Rico Teachers Association.
 Teams based in San Juan have been notably successful in athletic competition. The Santurce Crabbers (basketball), Santurce Crabbers won the National Superior Basketball League championship in 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001 and 2003 during this period being recognized as a dynasty. The San Juan Senators and the Santurce Crabbers (baseball), Santurce Crabbers were the two major baseball teams in the city, winning the championship of the Puerto Rican Professional Baseball League a total of 17 times. The Santurce Crabbers are located third among teams with more championships in the
Teams based in San Juan have been notably successful in athletic competition. The Santurce Crabbers (basketball), Santurce Crabbers won the National Superior Basketball League championship in 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001 and 2003 during this period being recognized as a dynasty. The San Juan Senators and the Santurce Crabbers (baseball), Santurce Crabbers were the two major baseball teams in the city, winning the championship of the Puerto Rican Professional Baseball League a total of 17 times. The Santurce Crabbers are located third among teams with more championships in the